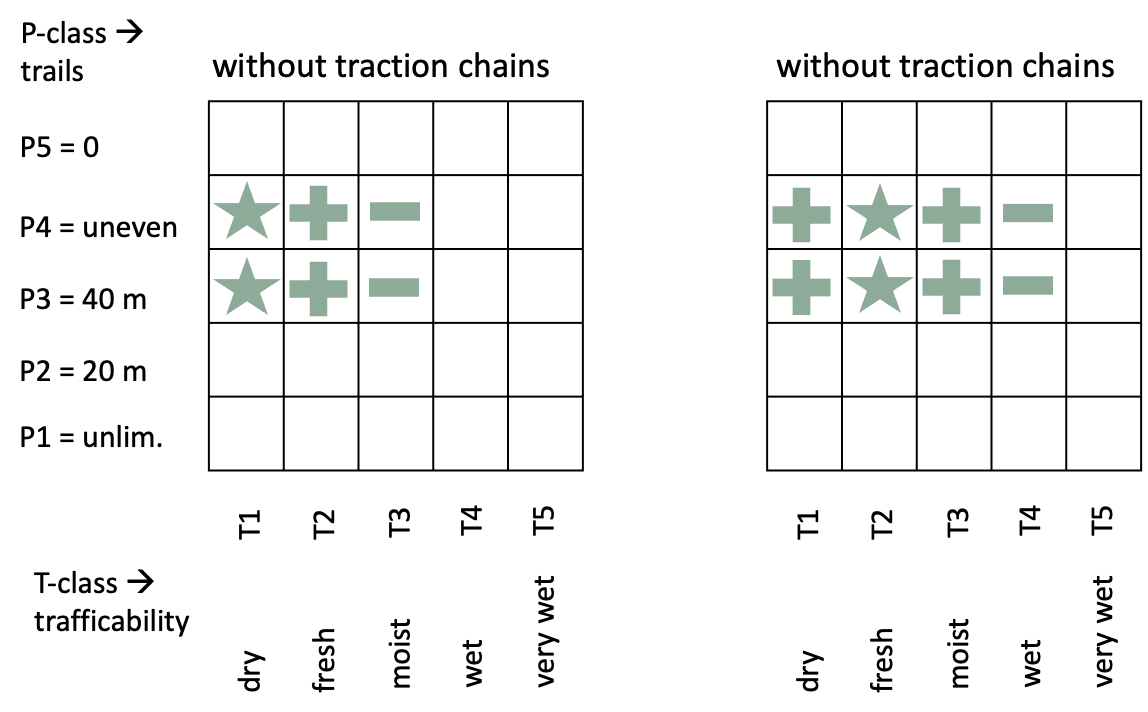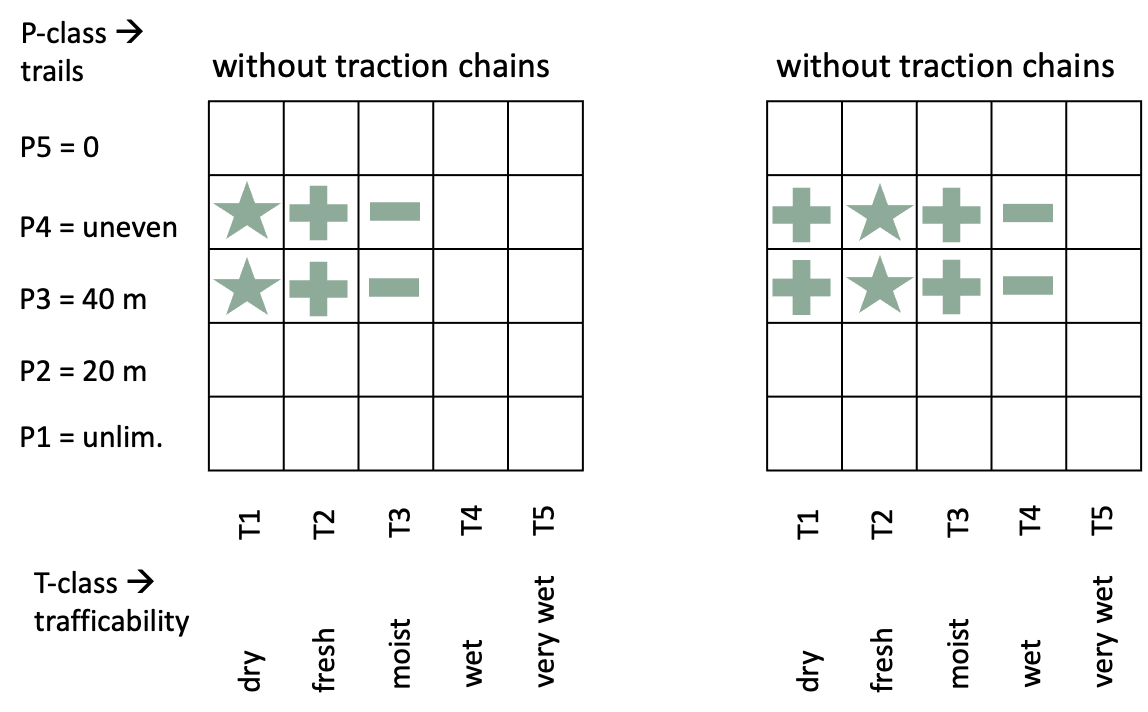Technodiversity glossary is a result of the ERASMUS+ project No. 2021-1-DE01-KA220-HED-000032038.
The glossary is linked with the project results of Technodiversity. It has been developed by
Jörn Erler, TU Dresden, Germany (project leader); Clara Bade, TU Dresden, Germany; Mariusz Bembenek, PULS Poznan, Poland; Stelian Alexandru Borz, UNITV Brasov, Romania; Andreja Duka, UNIZG Zagreb, Croatia; Ola Lindroos, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Mikael Lundbäck, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Natascia Magagnotti, CNR Florence, Italy; Piotr Mederski, PULS Poznan, Poland; Nathalie Mionetto, FCBA Champs sur Marne, France; Marco Simonetti, CNR Rome, Italy; Raffaele Spinelli, CNR Florence, Italy; Karl Stampfer, BOKU Vienna, Austria.
The project-time was from November 2021 until March 2024.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
SP-13-23 mechanized pre-skidding of short logsWhen trees are cross-cut at the felling site, the logs must be pre-skidded to the trail separately. This is only rational when the weight of the tree length is too high. For example, the basic log can be separated from the rest of the stem before pre-skidding. 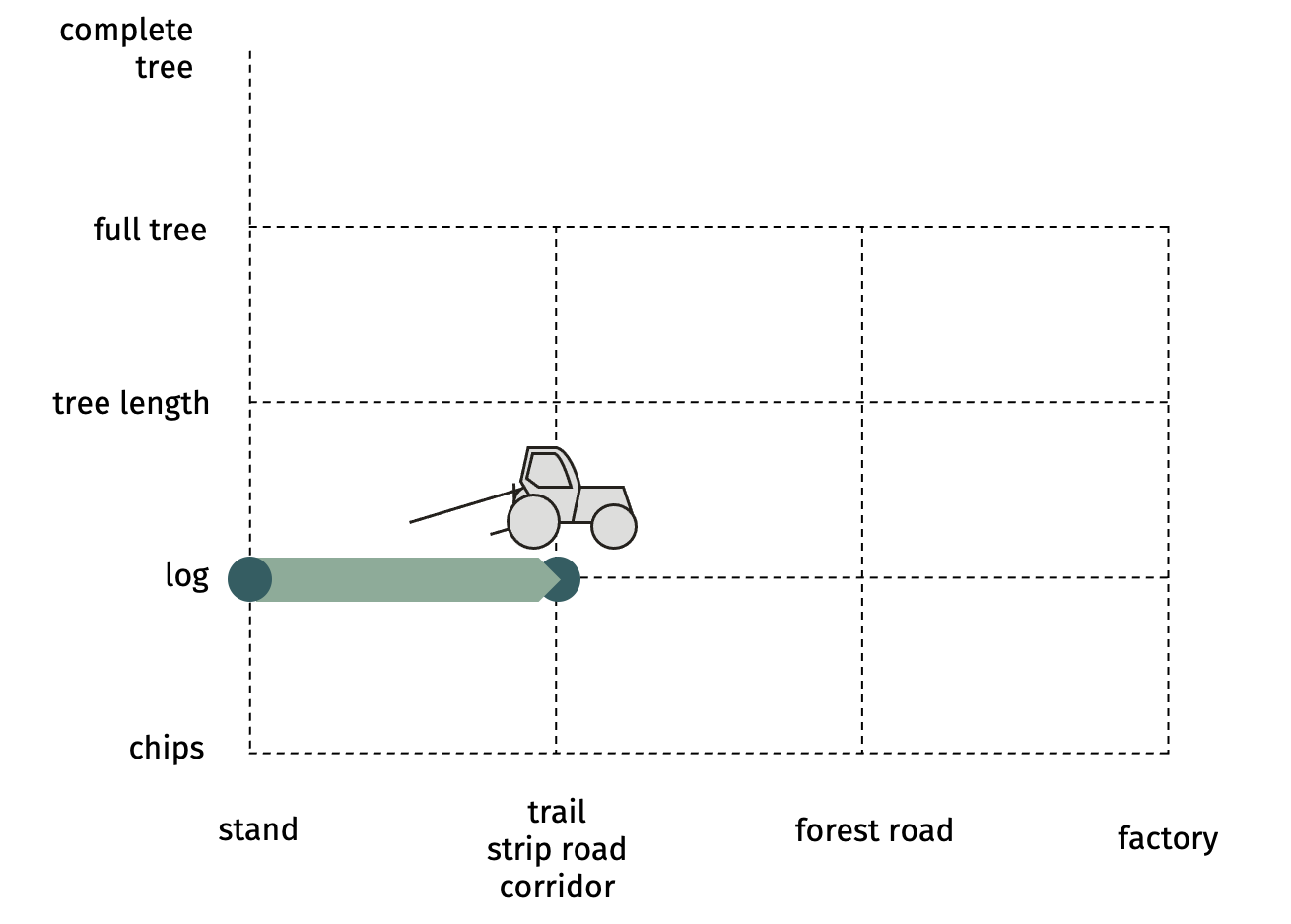 Advantages
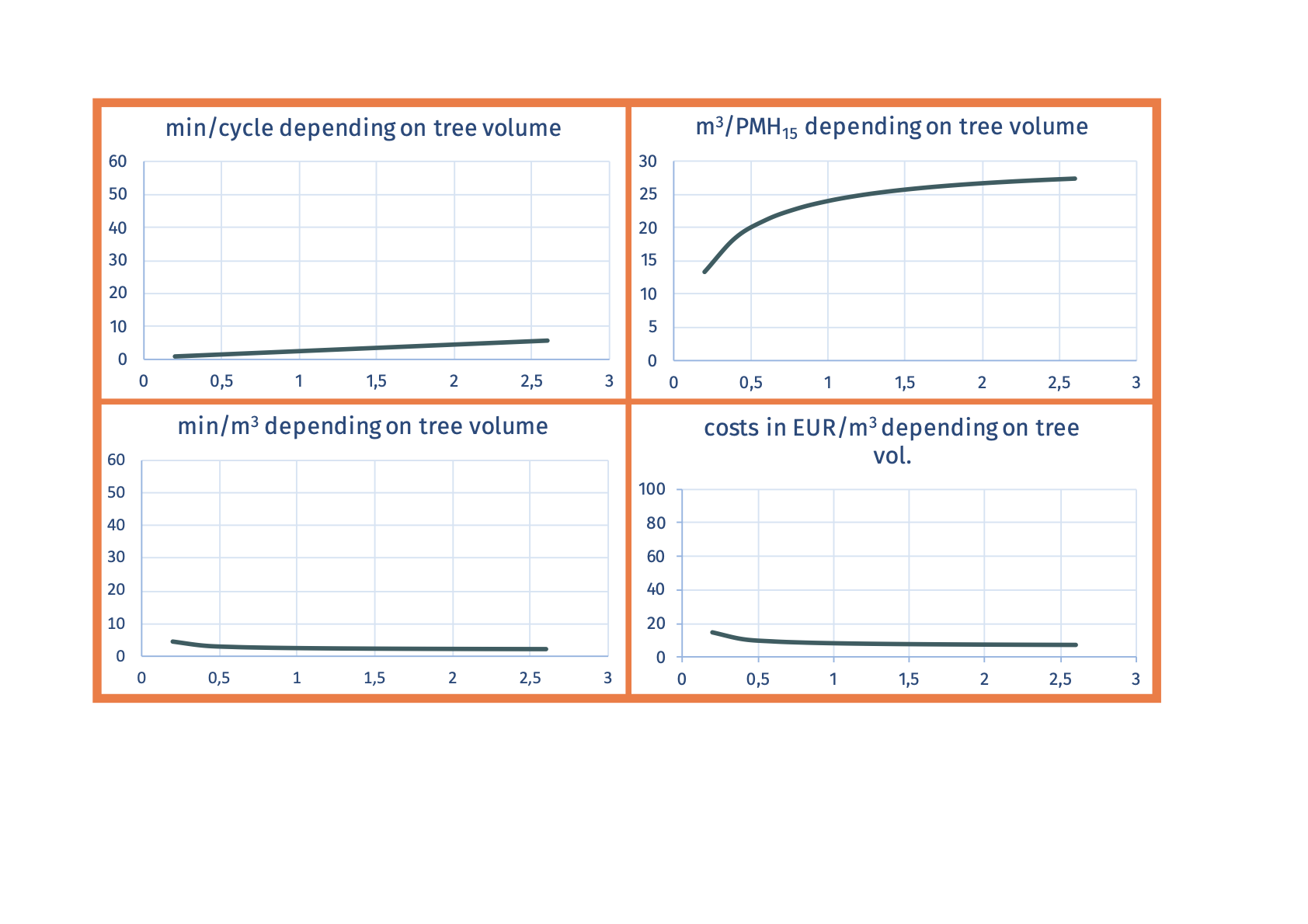
Minutes per cycle Example:
 Ecograms
Social suitability:
| |
SP-21-22 delimbingsee SP-x1-x2 delimbing | |
SP-21-23 mechanized processing on the trailProcessor (or harvester) standing on skid road processing the full tree that is laying down in reach of feeding device. The processing includes measuring, forecasting dimension, suggesting assortments, delimbing and cross-cutting. 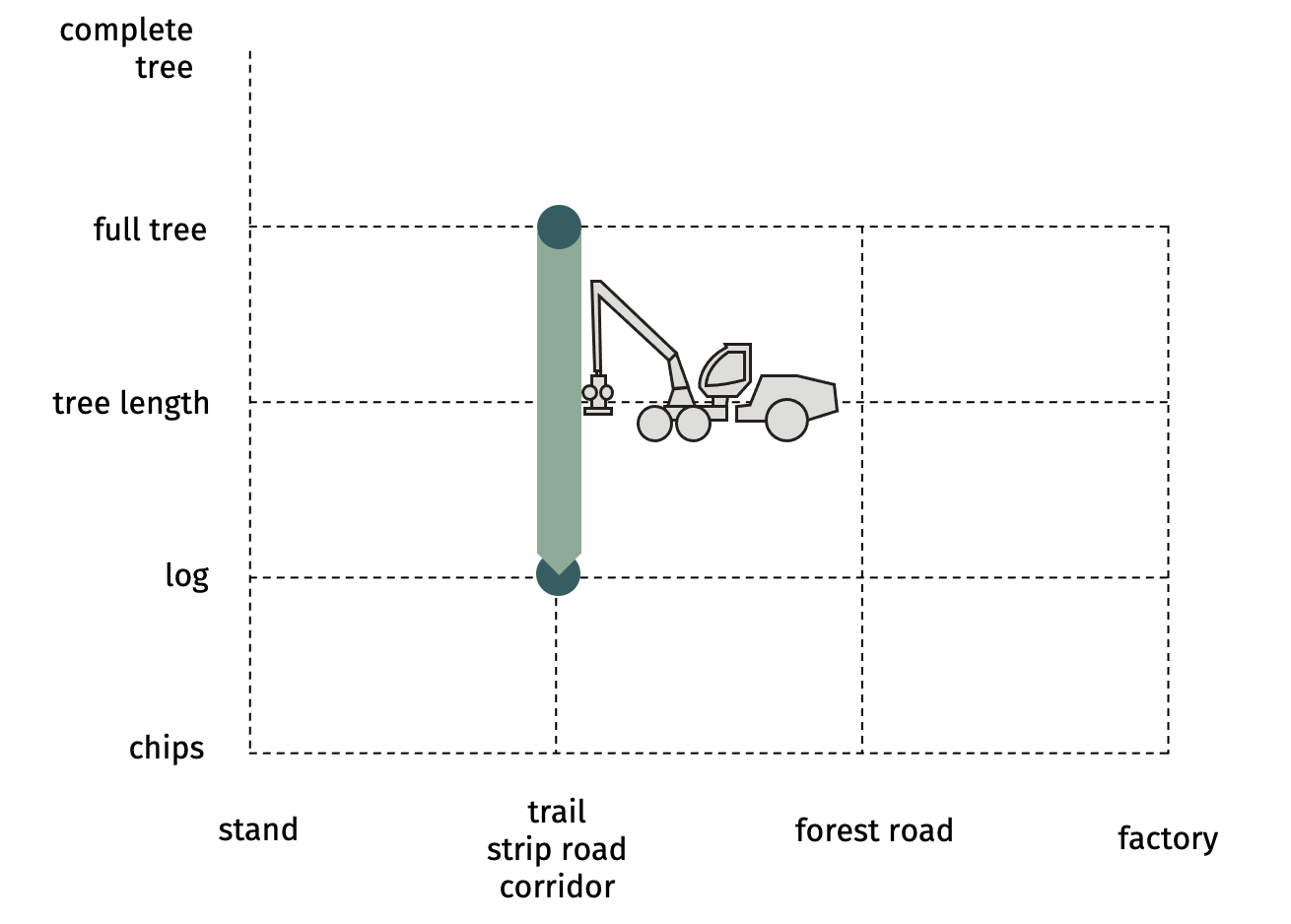 Advantages
Example:
 Ecograms
Social suitability
| |
SP-21-31 mechanized skidding of full tree with grapple skidderFull trees are dragged to the roadside landing by a machine that uses a grapple to collect the trees. 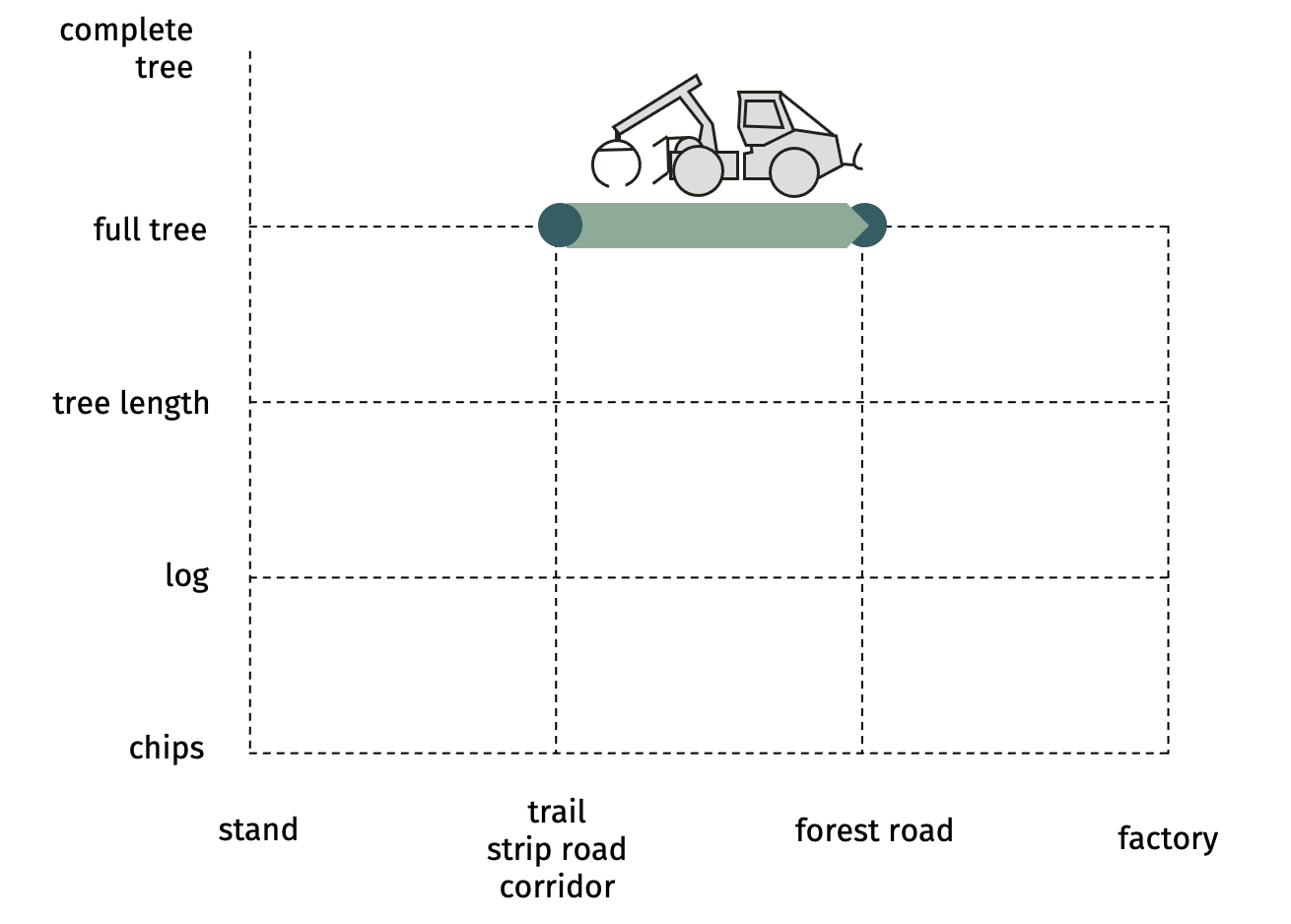 Advantages
Example:
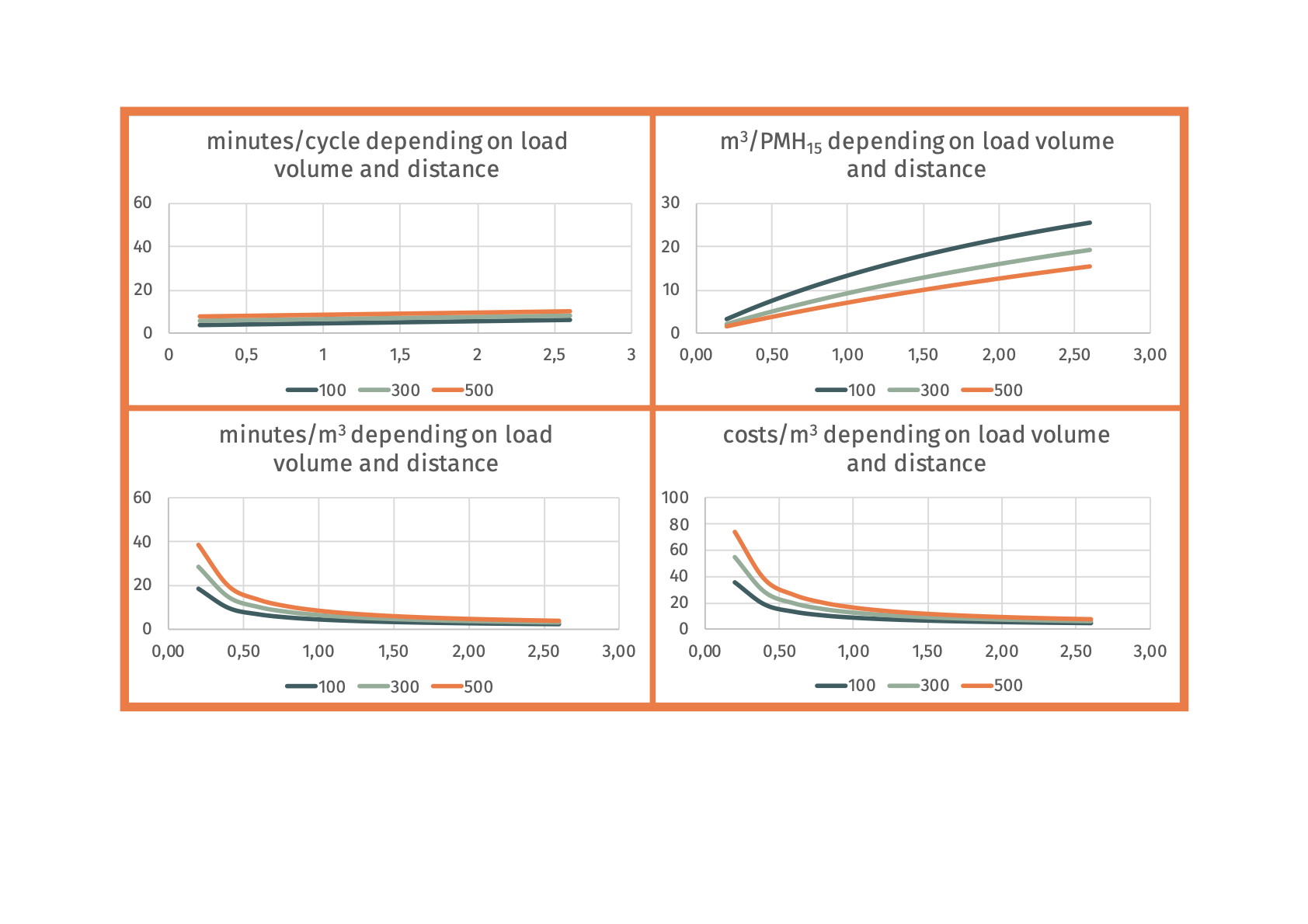 Ecograms
Social suitability:
| |
SP-21-31 mechanized skidding of full trees with skidderFull trees are
dragged to the roadside landing by a tractor (dedicated skidder, crawler,
forestry fitted farm tractor) using chains or cable. 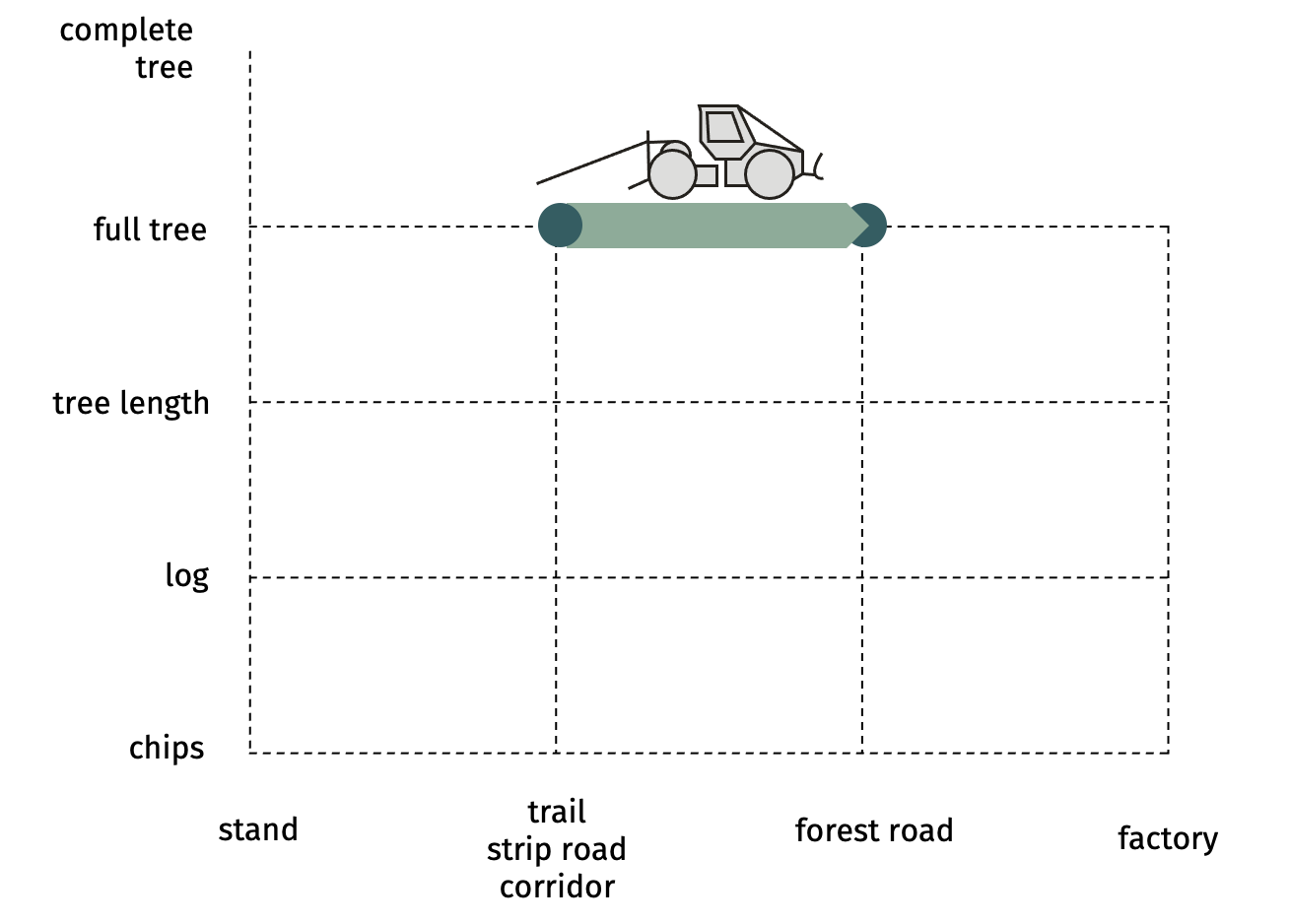 Advantages
Example:
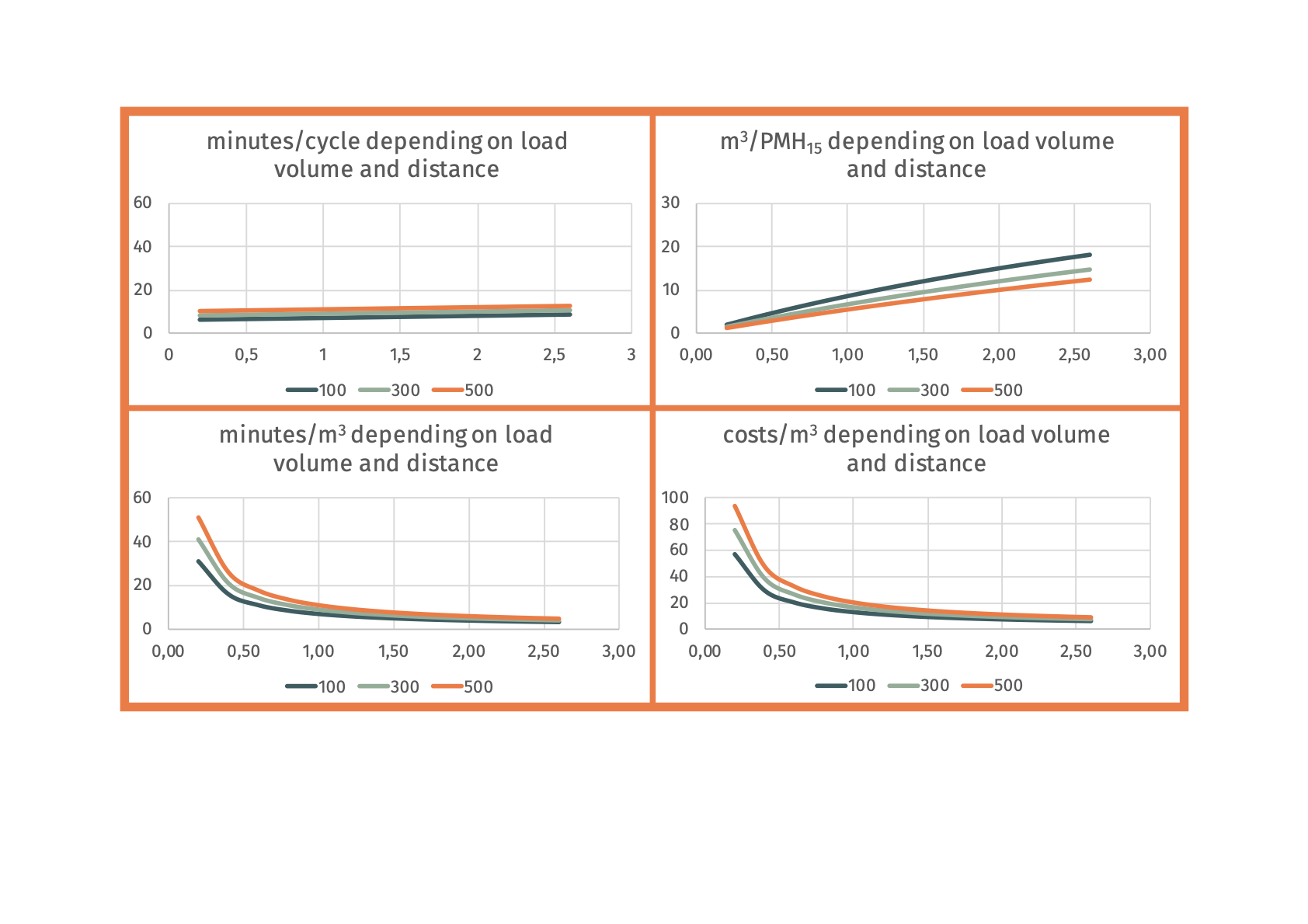 Ecograms
Social suitability:
graph from Ecotrac study and Rien's lesson (re-conduce everything to tree size m3 on the x-axis, then different lines for different distances and maybe one graph for small skidder and one for large skidder) | |
SP-21-31 skidding of full tree with clam-bunk skidderFull trees are
skidded with their butts resting on the rear axle of the skidder, while tree
tops drag on the ground. The butts
are retained on top of the rear axle by an inverted grapple (clambunk) and
placed on that grapple using a hydraulic loader. Functiogram 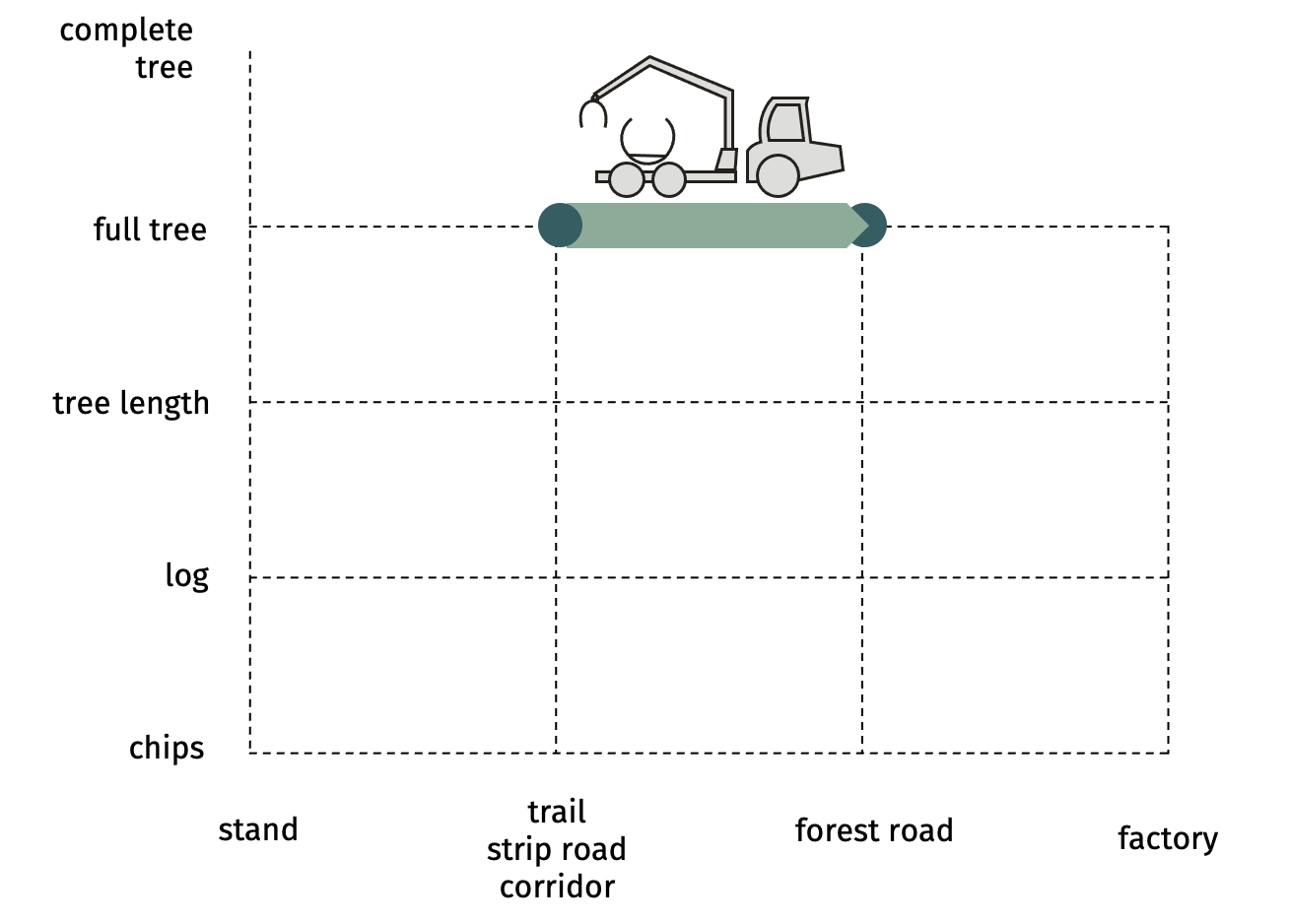 Advantages
Example:
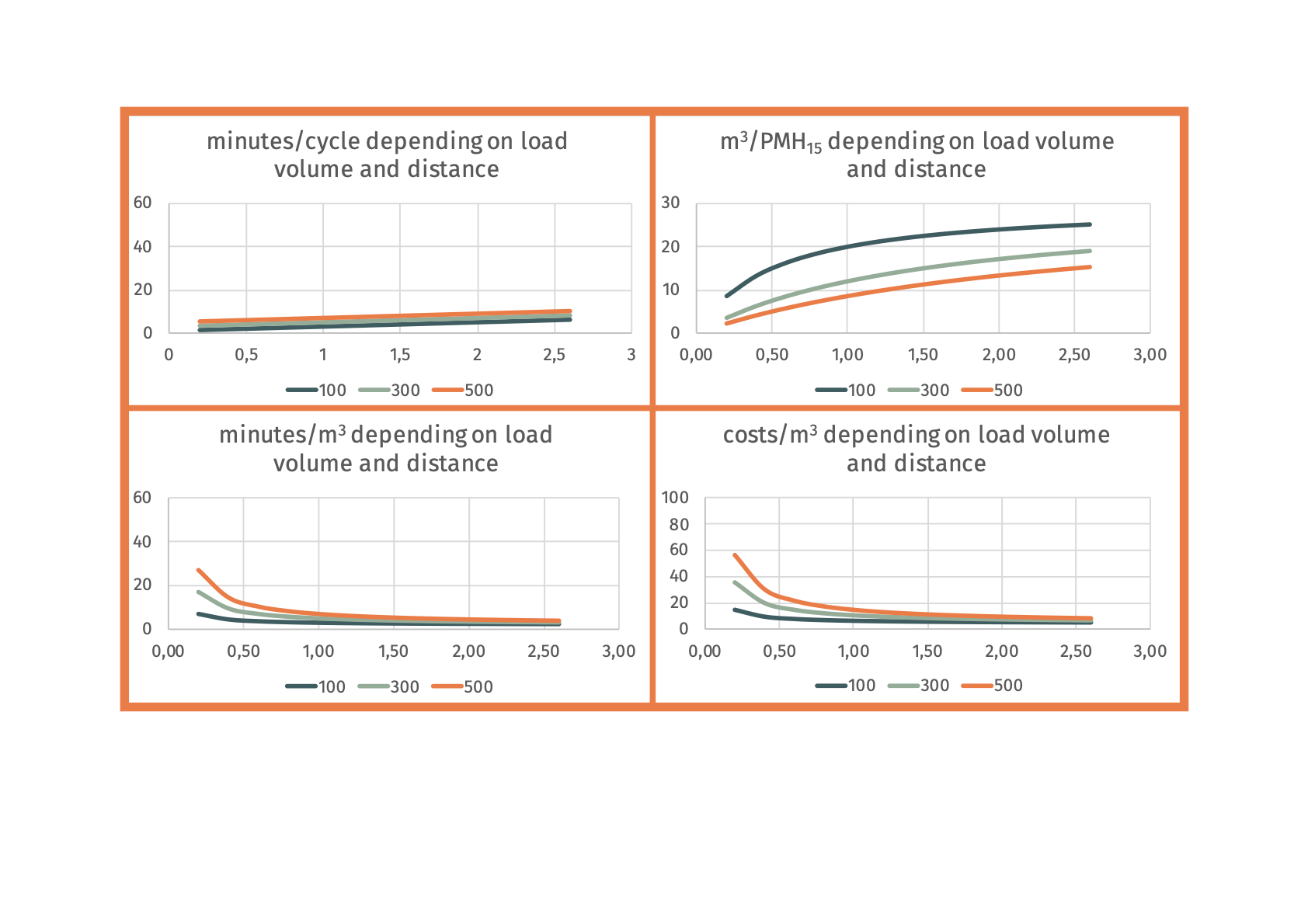 Ecograms
Social suitability:
| |
SP-21-34 mechanized chipping of full trees on the trailFull trees that are laid down alongside the trail are chipped by a self-propelled chipper or a tractor powered chipper with terrain capability. Chips are blown into an integral bin and then transferred to a chip shuttle (forwarder-based) or into a bin trailer, towed by the same tractor or by an accompanying tractor. 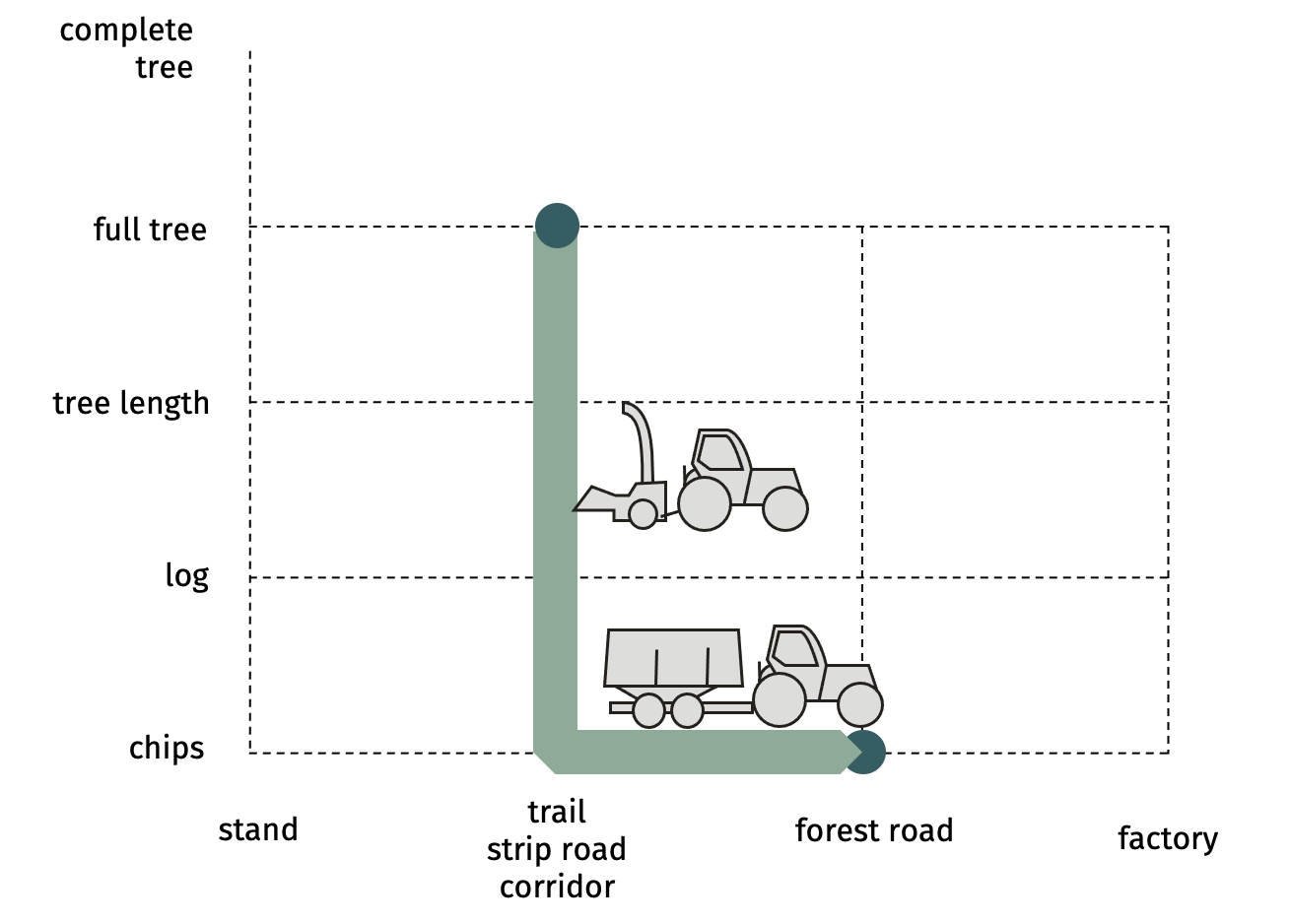 Advantages
Example:
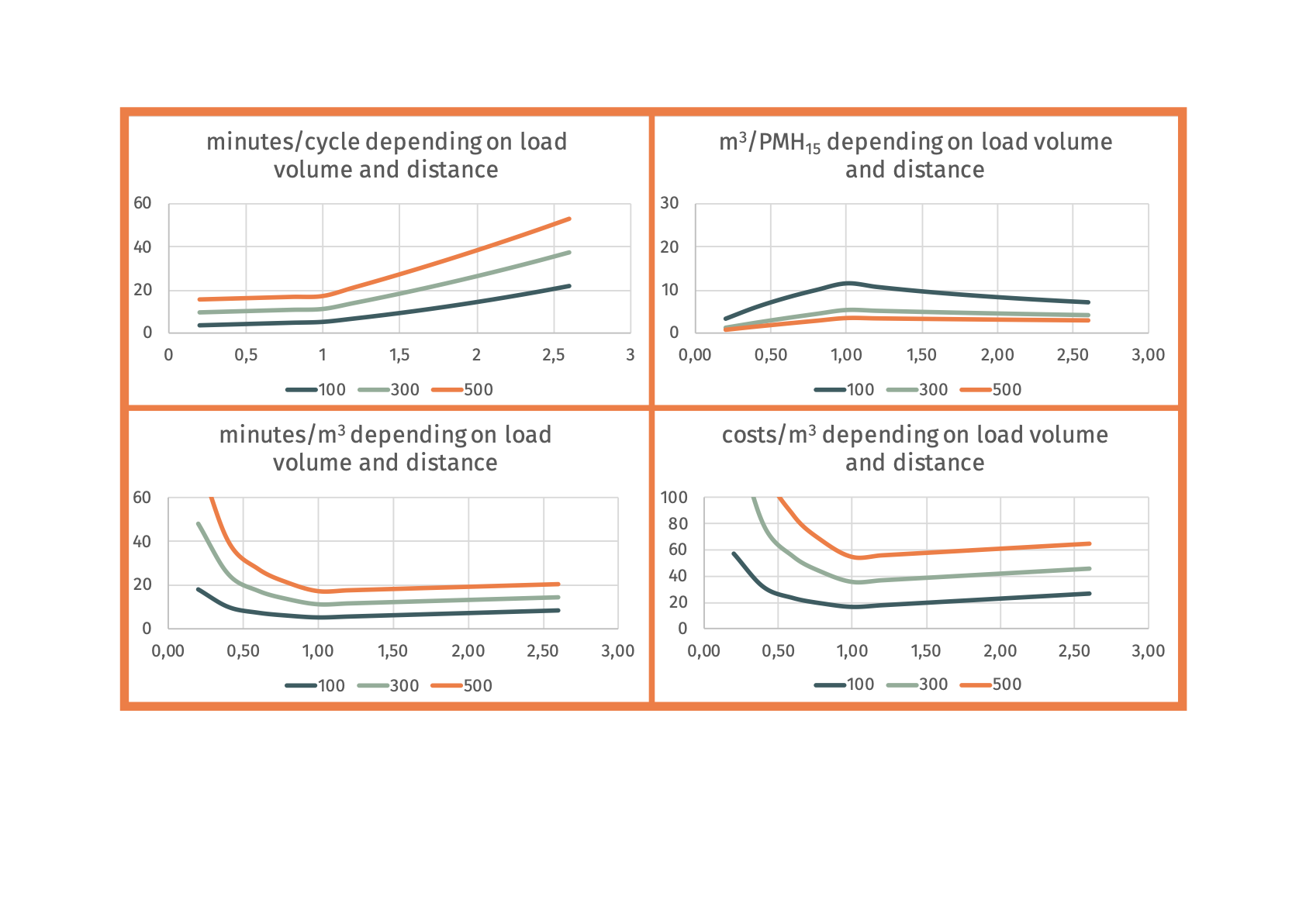 Ecograms
Literature: Check Waterford studies | |
SP-22-23 cross-cuttingsee SP-x2-x3 cross-cutting | |
SP-22-32 mechanized skidding of tree lengths with clam-bunk skidderTree lengths that are pre-skidded to the trail are skidded to the forest road using a clam-bunk skidder. This includes: loading the trees with the crane into the clam-bunk, skidding them to forest road, storing them alongside road or a landing. 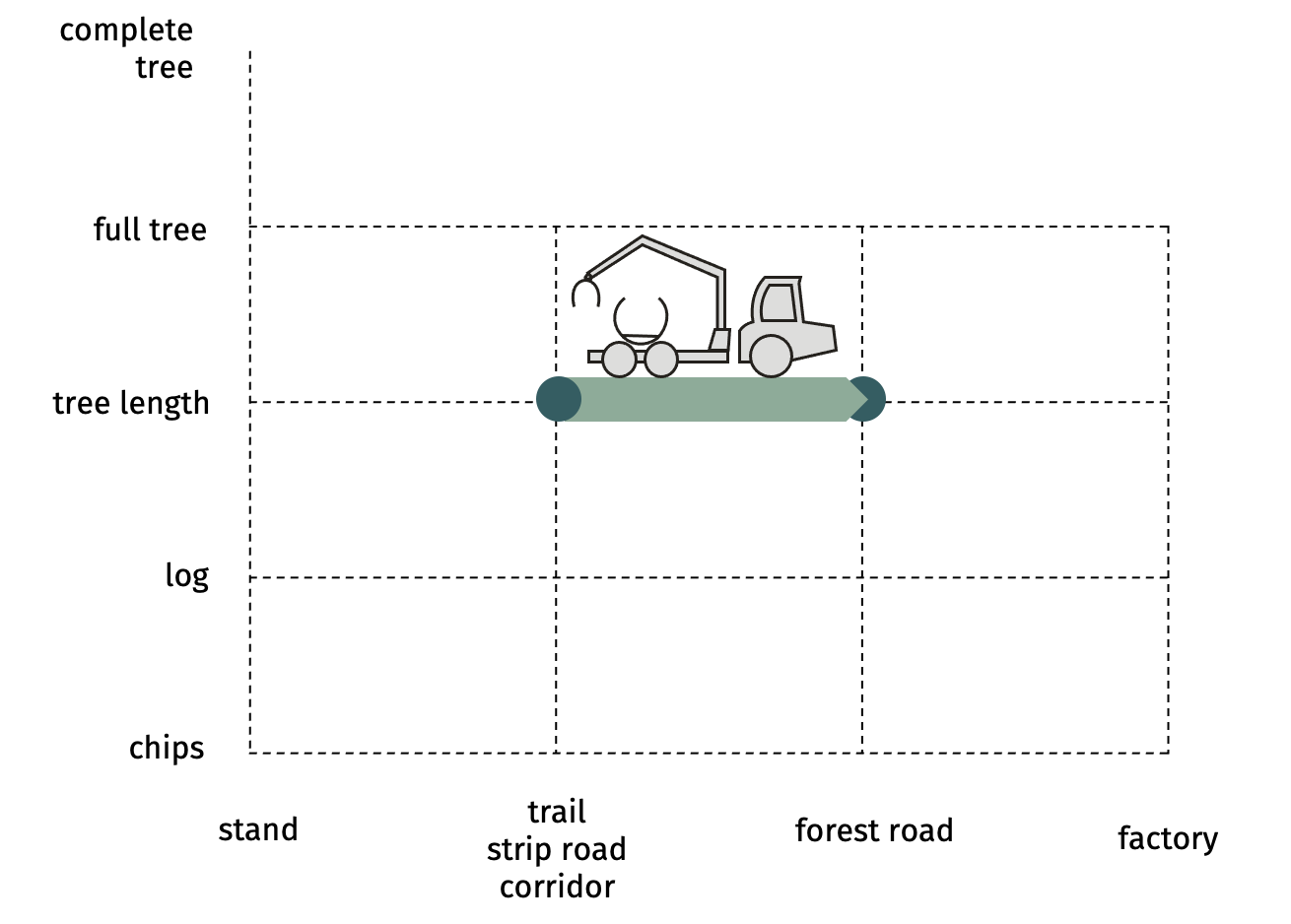 Advantages
Example:
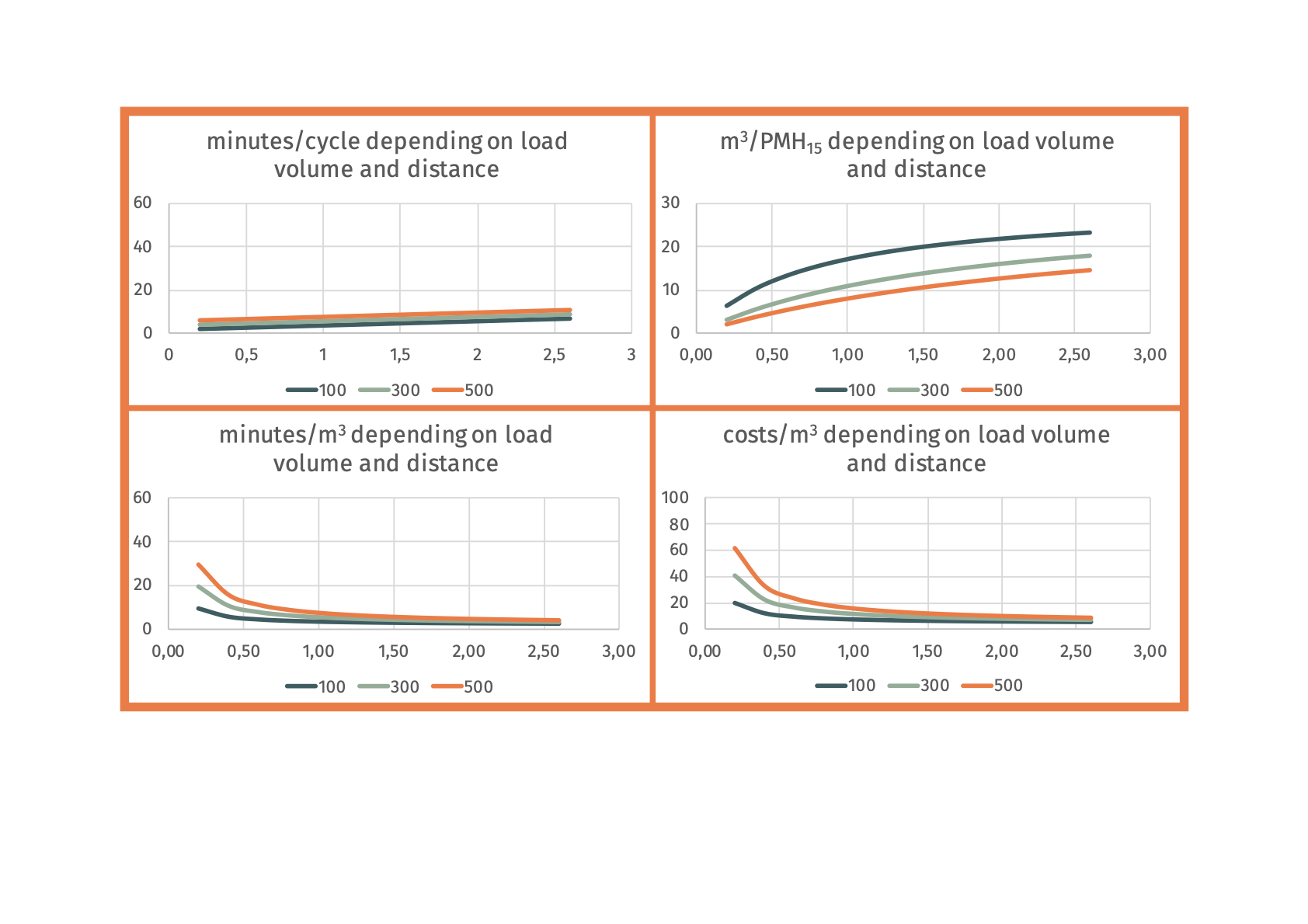 Ecograms
Social suitability
Logging arch study for farm tractors - Merlo study etc. | |
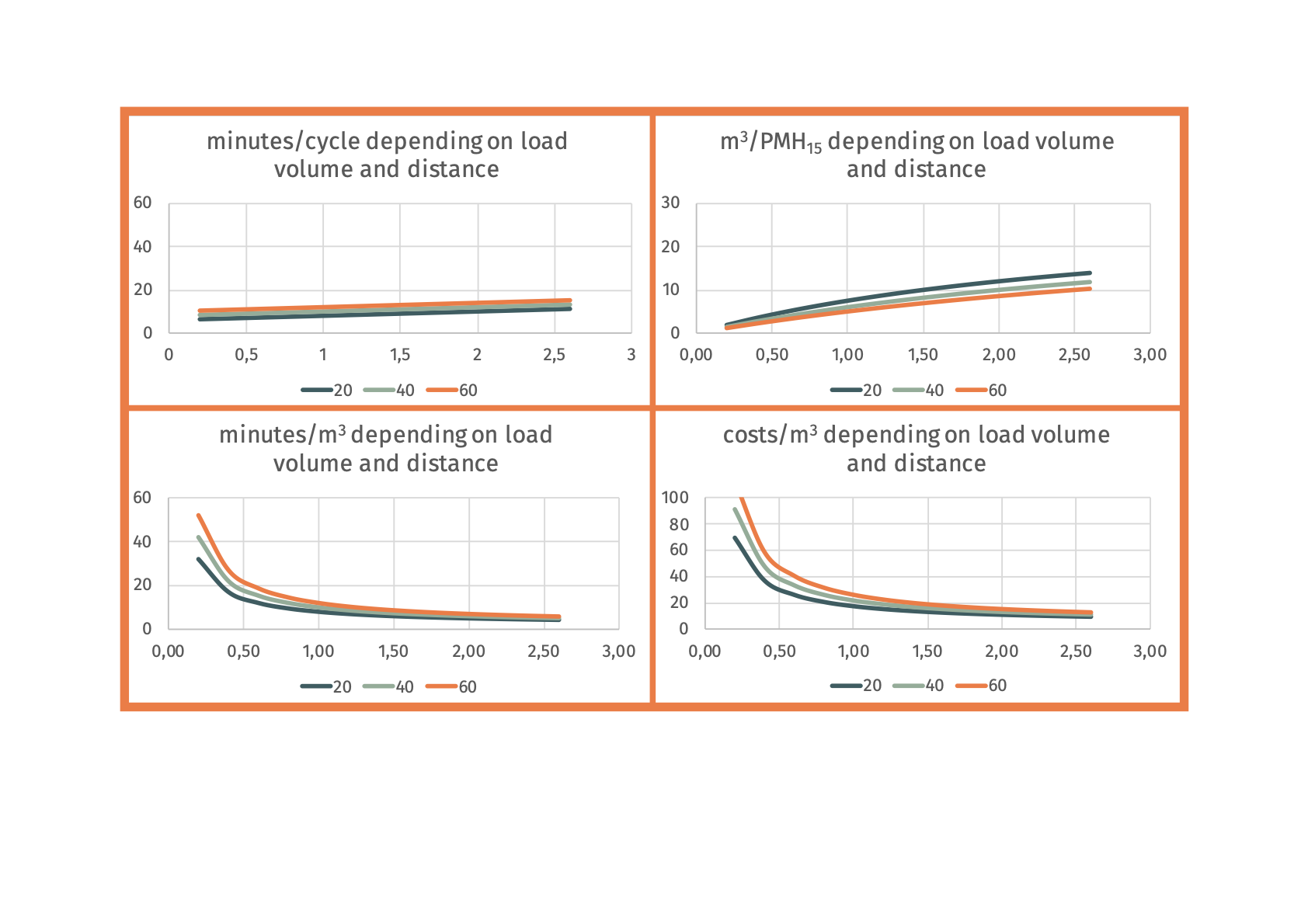
SP-22-32 mechanized skidding of tree lengths with skidderTree lengths that are pre-skidded to the trail are skidded to the forest road. This includes: setting chokers on several tree-lengths to optimize the load, skidding them to forest road, storing them alongside road or a landing. 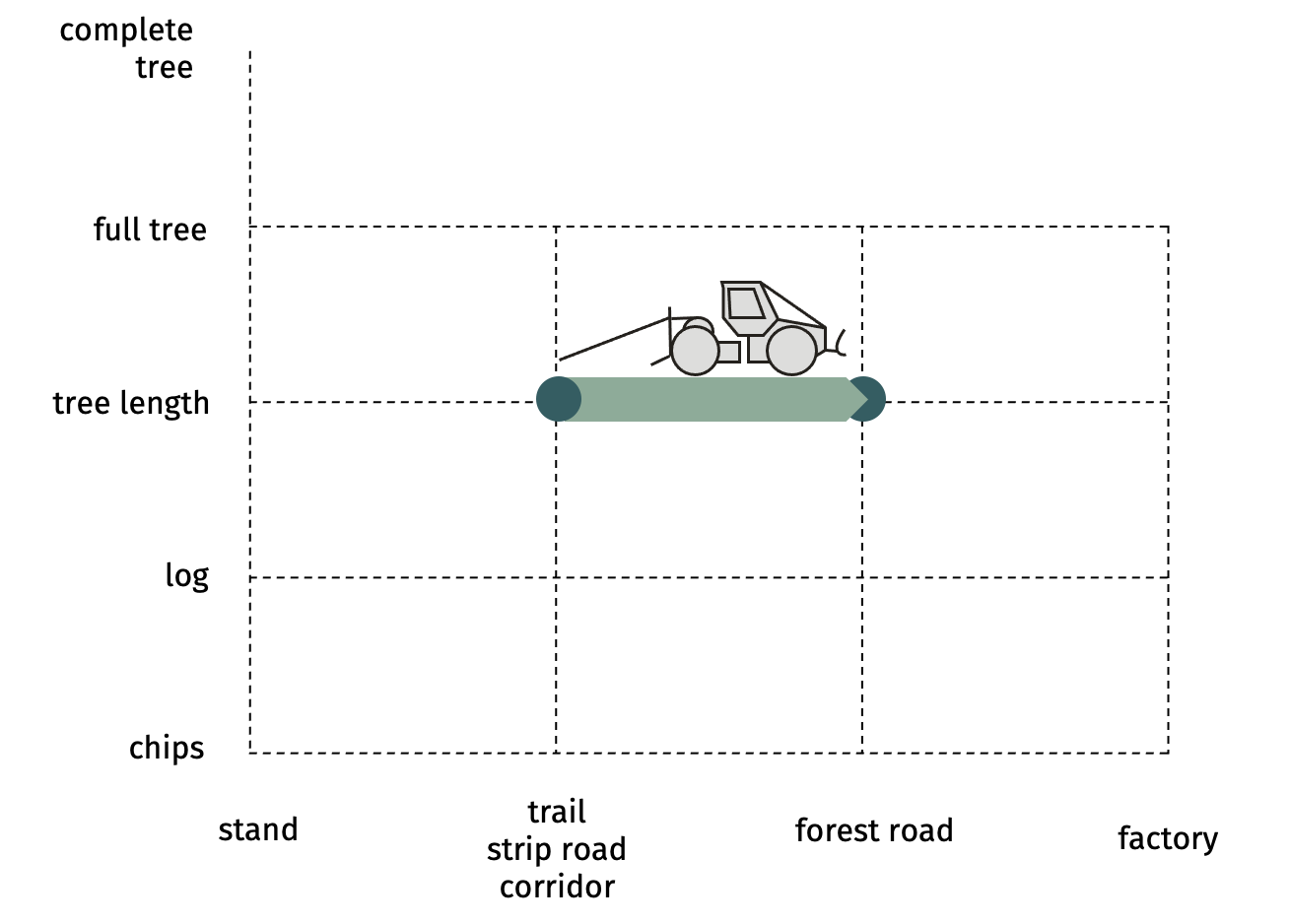 Advantages
Minutes per cycle Example:
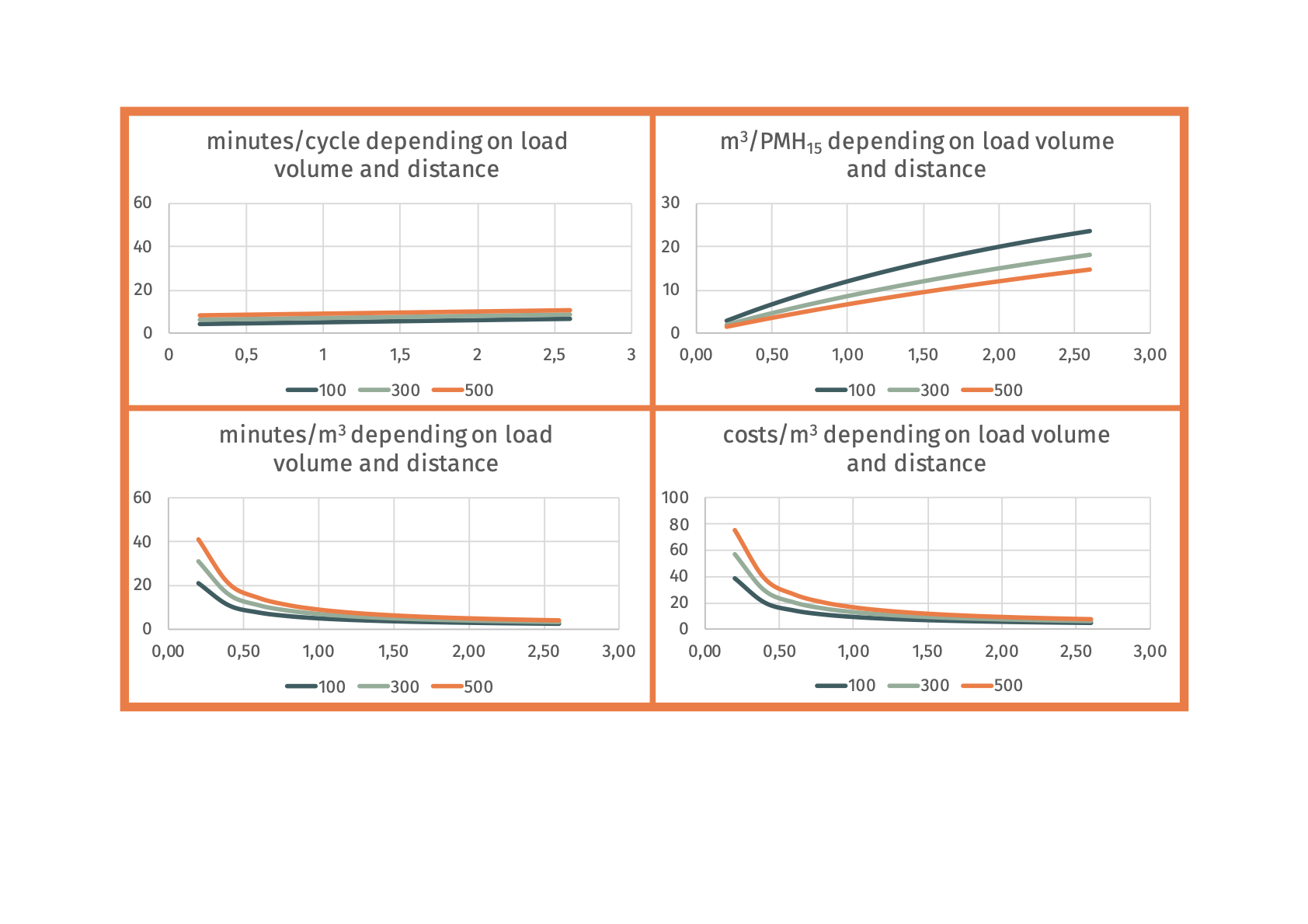 Ecograms
Social suitability
| |