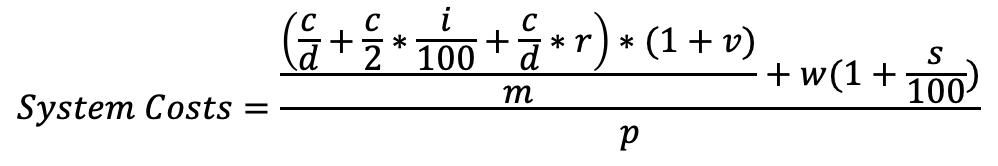Technodiversity glossary is a result of the ERASMUS+ project No. 2021-1-DE01-KA220-HED-000032038.
The glossary is linked with the project results of Technodiversity. It has been developed by
Jörn Erler, TU Dresden, Germany (project leader); Clara Bade, TU Dresden, Germany; Mariusz Bembenek, PULS Poznan, Poland; Stelian Alexandru Borz, UNITV Brasov, Romania; Andreja Duka, UNIZG Zagreb, Croatia; Ola Lindroos, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Mikael Lundbäck, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Natascia Magagnotti, CNR Florence, Italy; Piotr Mederski, PULS Poznan, Poland; Nathalie Mionetto, FCBA Champs sur Marne, France; Marco Simonetti, CNR Rome, Italy; Raffaele Spinelli, CNR Florence, Italy; Karl Stampfer, BOKU Vienna, Austria.
The project-time was from November 2021 until March 2024.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
V |
|---|
Variable costsVariable costs are a part of the cost calculation with the engineering formula. They consider those costs that only occur when the system is working. When it stands by, these costs are zero. But when the machine works, it consumes energy in the form of fuel or electricity, plus other consumables like hydraulic oil, lubricants, and so on. It is not too difficult to calculate these costs per hour. With fuel, we multiply consumption (liters per hour) with the price per liter, for example. For a general approximation, one can also take the sum of fixed costs and multiply it with nay estimated factor. With expensive machines it is roughly 10%, and it climbs up to 50% with simple machines like the chainsaw. (See more at TDiv PR1-C02)
 | |