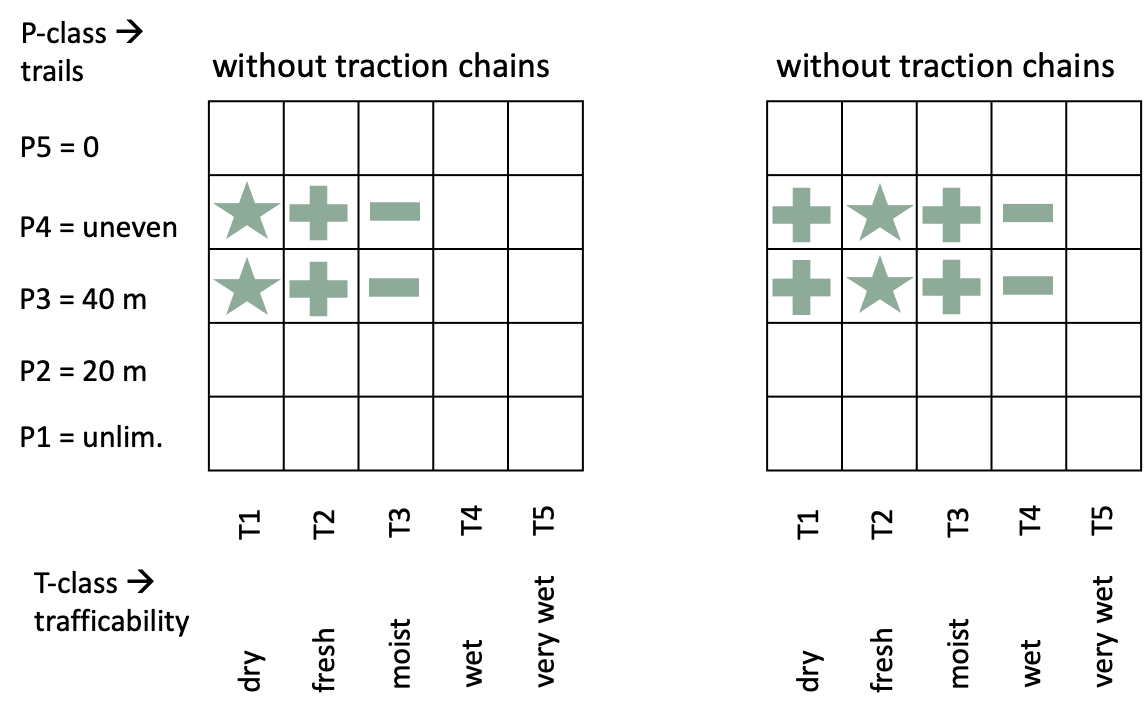Technodiversity glossary is a result of the ERASMUS+ project No. 2021-1-DE01-KA220-HED-000032038.
The glossary is linked with the project results of Technodiversity. It has been developed by
Jörn Erler, TU Dresden, Germany (project leader); Clara Bade, TU Dresden, Germany; Mariusz Bembenek, PULS Poznan, Poland; Stelian Alexandru Borz, UNITV Brasov, Romania; Andreja Duka, UNIZG Zagreb, Croatia; Ola Lindroos, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Mikael Lundbäck, SLU Umeå, Sweden; Natascia Magagnotti, CNR Florence, Italy; Piotr Mederski, PULS Poznan, Poland; Nathalie Mionetto, FCBA Champs sur Marne, France; Marco Simonetti, CNR Rome, Italy; Raffaele Spinelli, CNR Florence, Italy; Karl Stampfer, BOKU Vienna, Austria.
The project-time was from November 2021 until March 2024.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
SP-23-34 mechanized chipping of residues on the trailLogs are
chipped by a self-propelled chipper or a tractor-powered chipper, fed by a
loader. Chips are blown into an integral bin, a bin trailer, towed by the same
tractor or by an accompanying machine. The most effective team is that composed by a
self-propelled chipper with integral loader and bin and a chip-shuttle
(forwarder-based eg. Silvatec)  Advantages
Example:
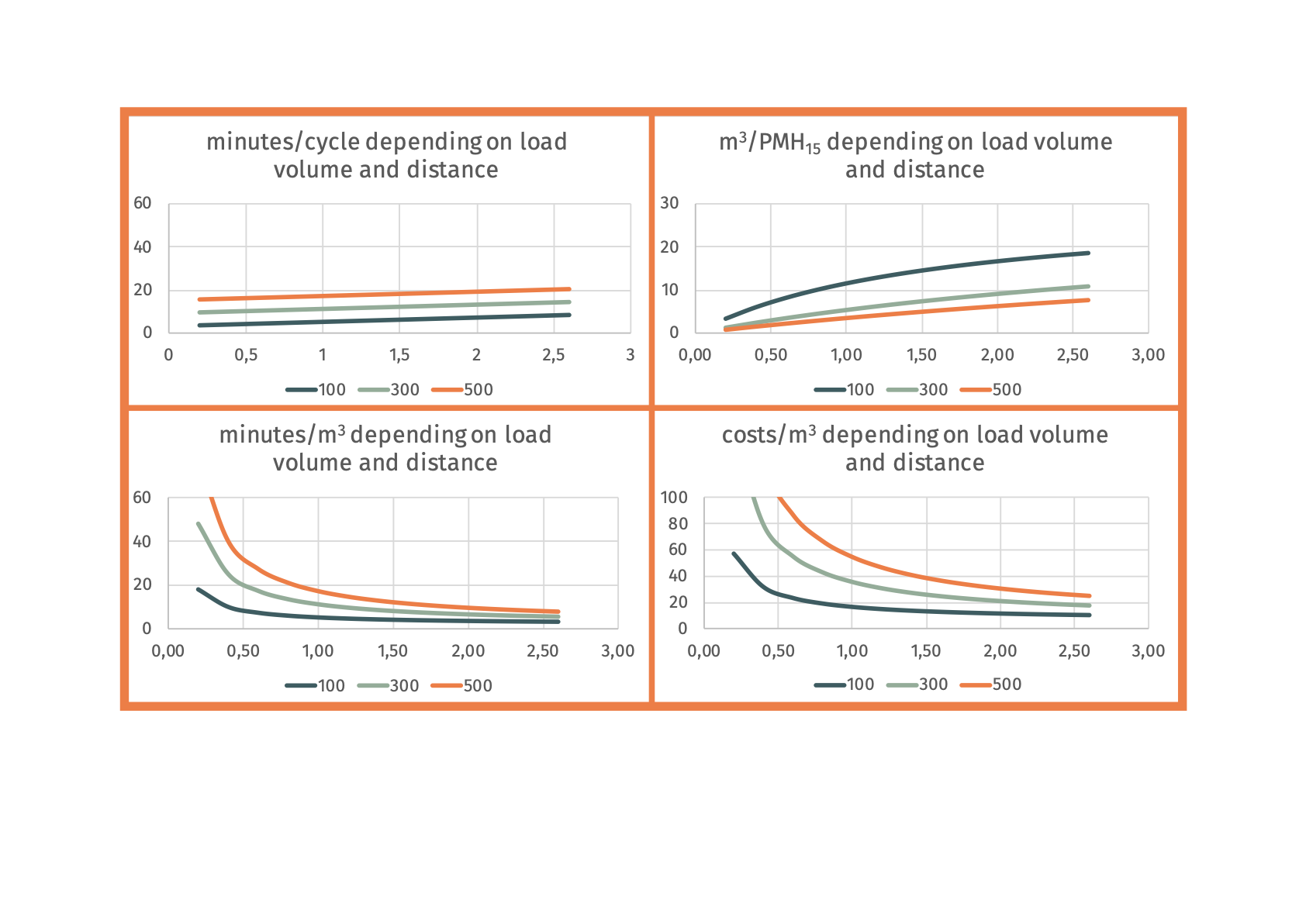 Ecograms
Literature: Spinelli & Hartsough 2001, Spinelli & Magagnotti 2010, and many more | |
SP-31-32 delimbingsee SP-x1-x2 delimbing | |
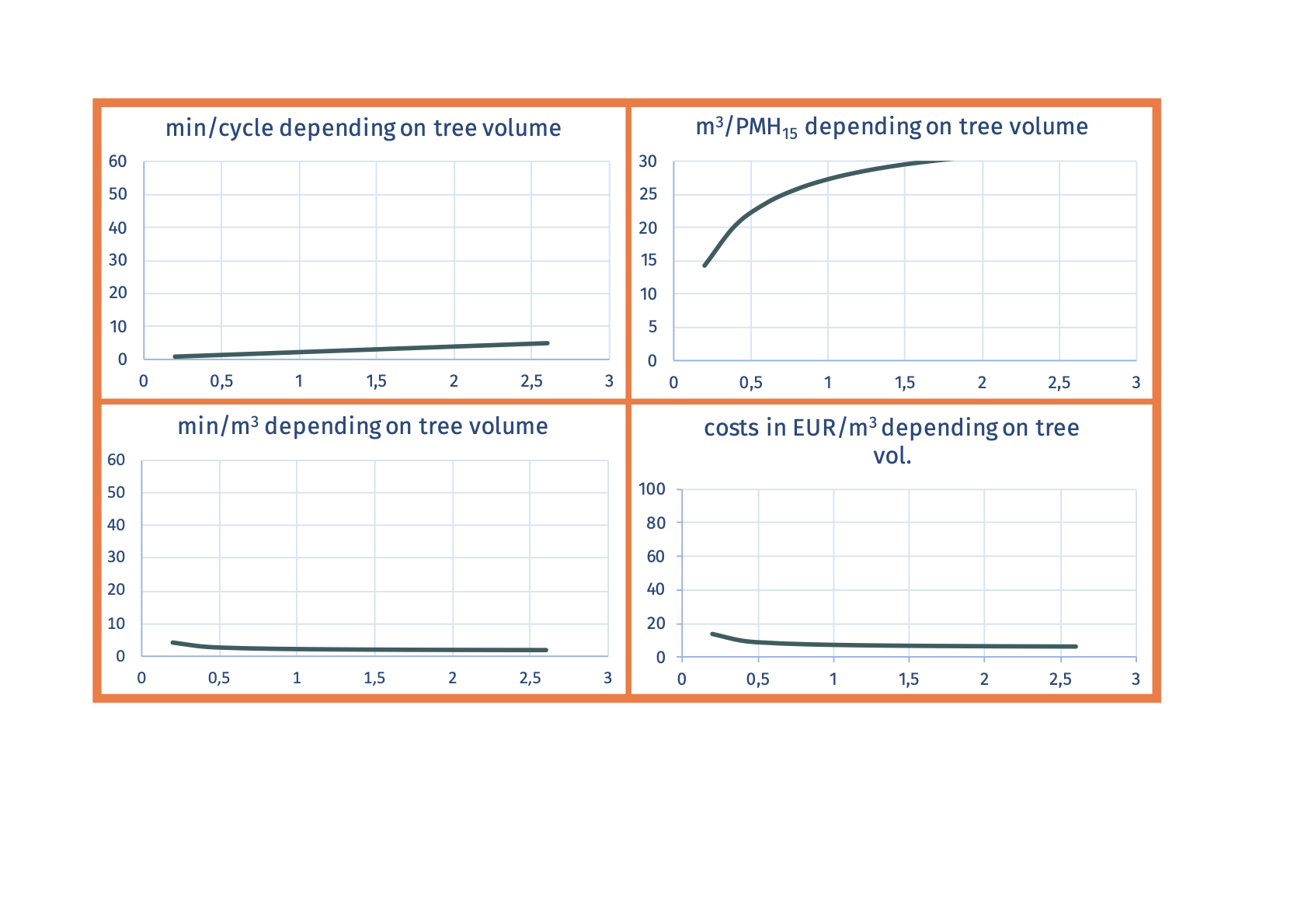
SP-31-33 mechanized processing on the forest roadProcessor
(or harvester) standing on forest road and processing
the skidded full trees, which are stored. 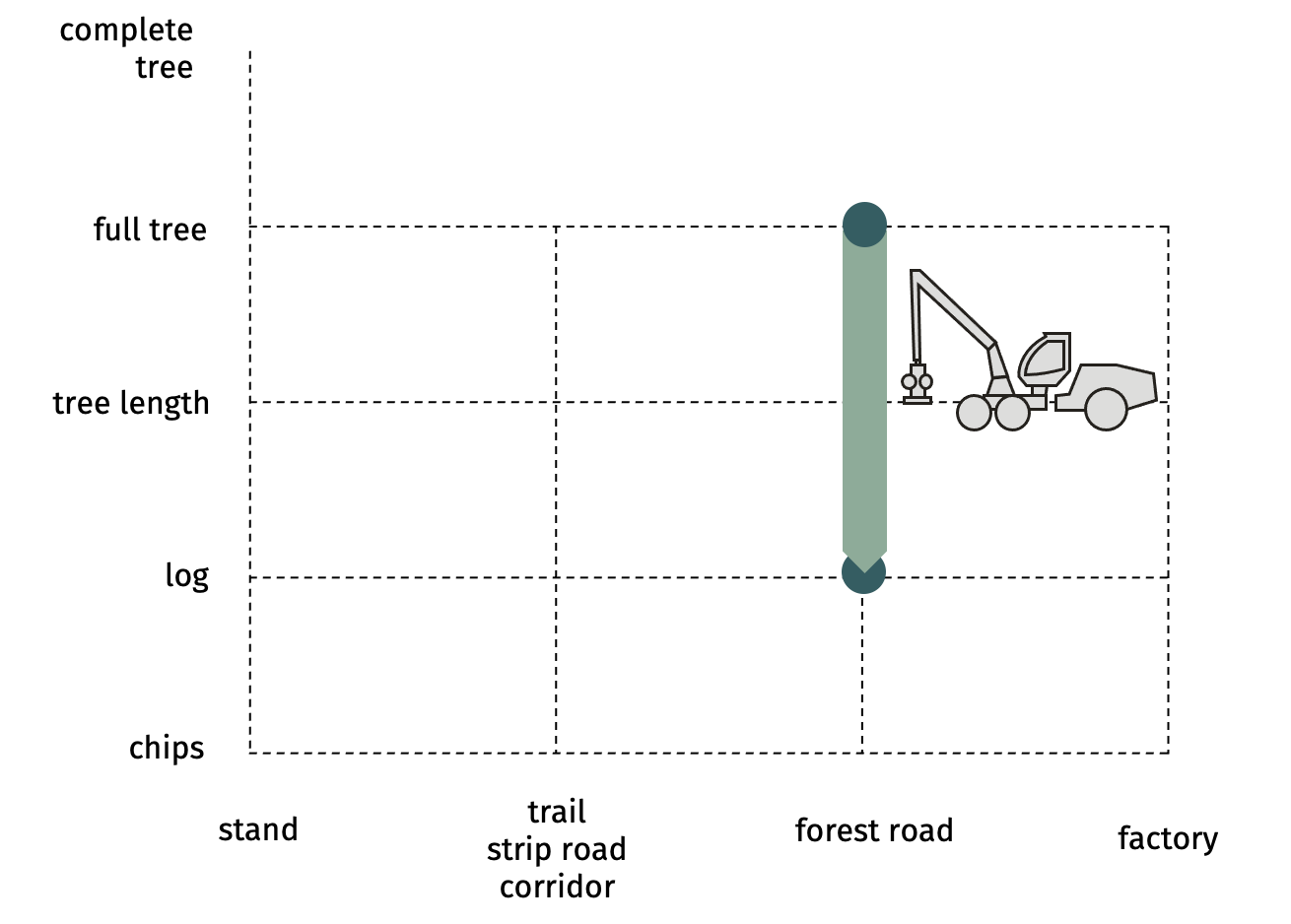 Advantages
Example:
 Ecogram
Social suitability:
| |
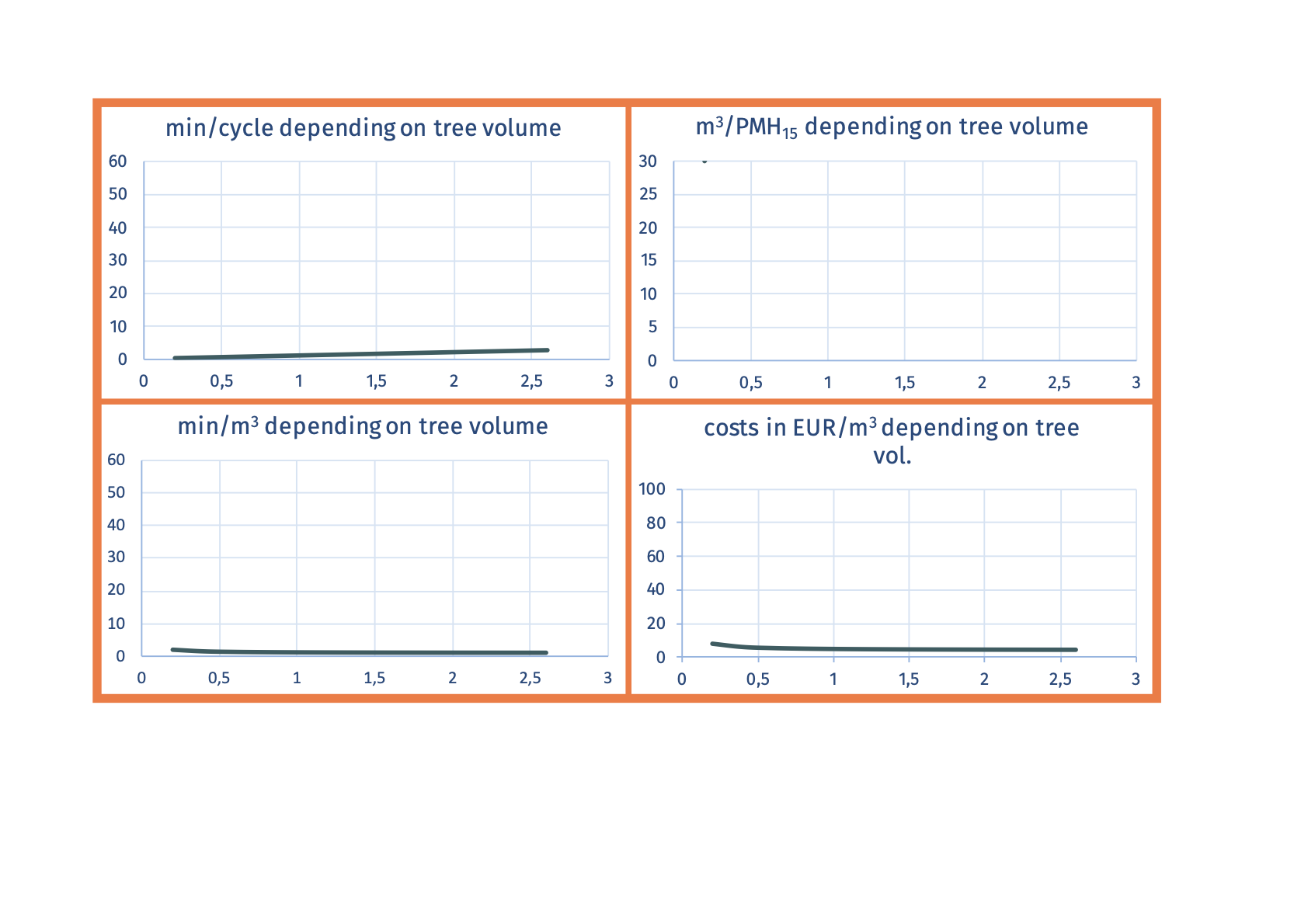
SP-31-34 mechanized chipping of full trees at forest roadFull trees are chipped at a roadside landing 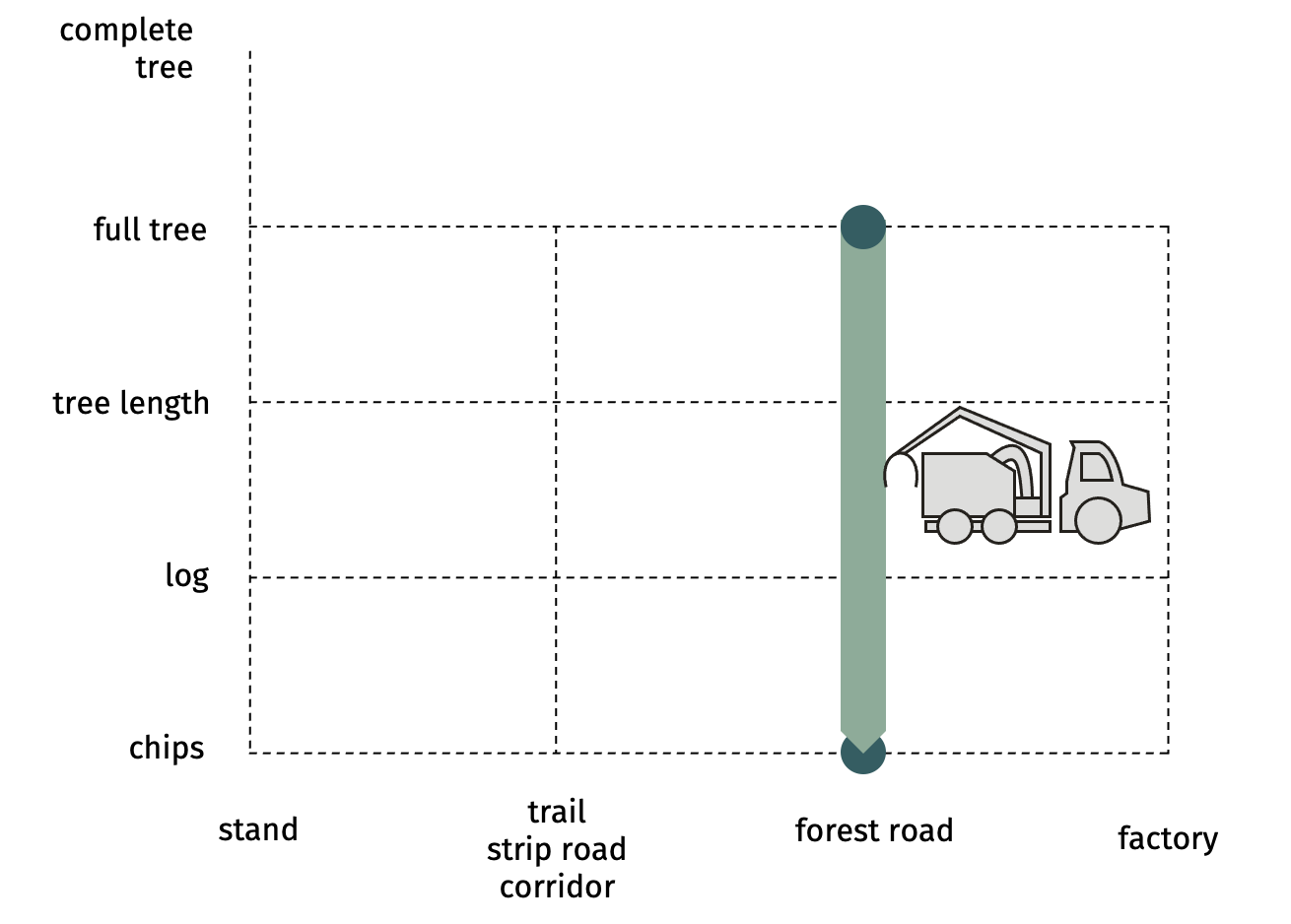 Advantages
Economic suitability Example:
 Ecogram
Social suitability
Literature: Eliasson, L., Von Hofsten, H., Johannesson, T., Spinelli, R., Tierfelder, T., 2015: Effects of sieve size on chipper productivity, fuel consumption and chip size distribution for open drum chippers. Croatian Journal of Forest Engineering 36: 11-17. | |
SP-32-33 cross-cuttingsee SP-x2-x3 cross-cutting | |
SP-32-34 mechanized chipping of tree lengths at forest roadTree lengths that are stored at the forest road are chipped.
Advantages
Example:
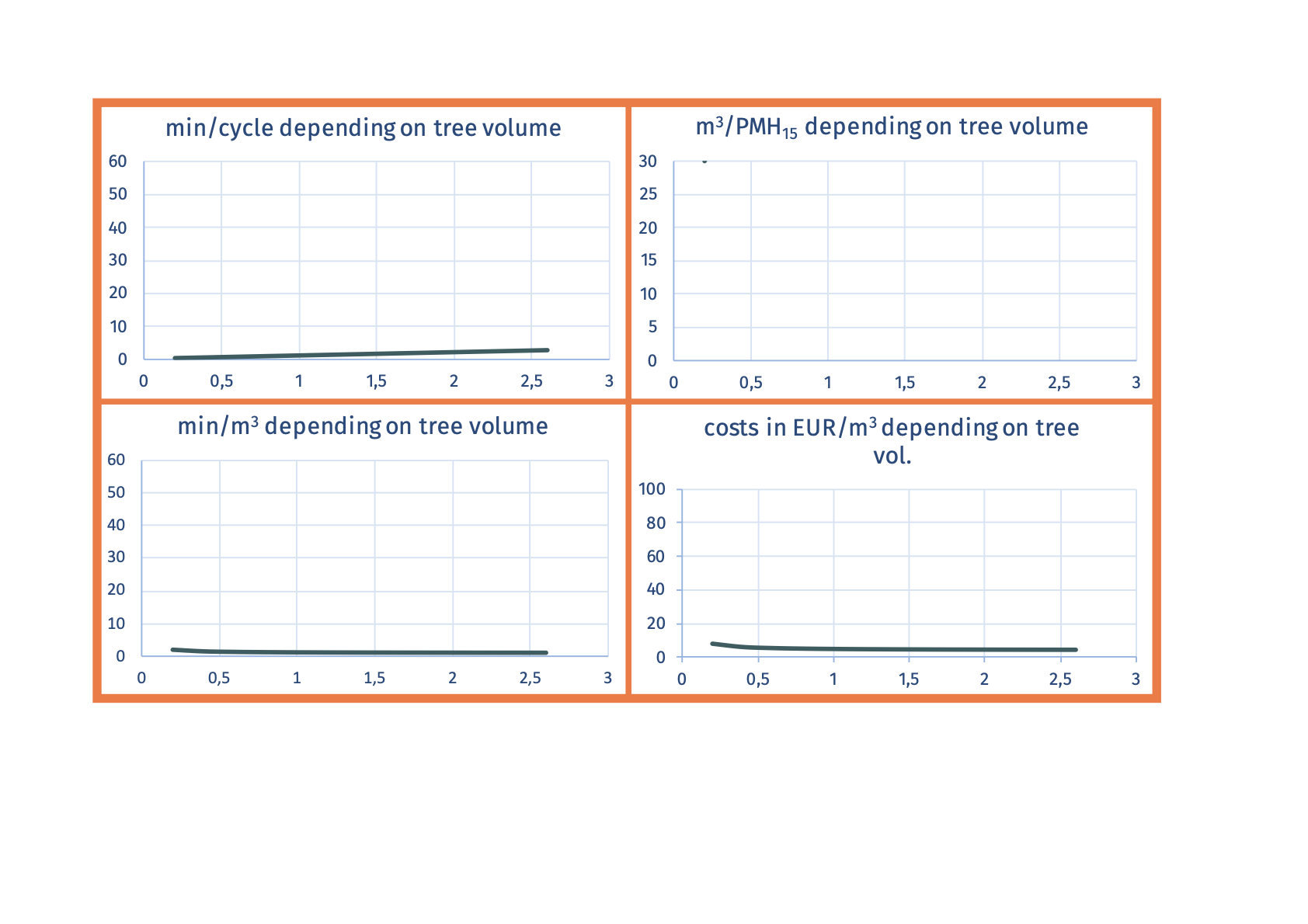 Ecogram
Social suitability
| |
SP-33-34 mechanized chipping of short logs at forest roadLogs are chipped from stacks piled at the roadside. The work can be done with any chipper, in any configurations. Chips can be discharged directly onto trucks, onto tractor- trailers or on the ground. Surge bins can also be used  Advantages
Advantages
Example:
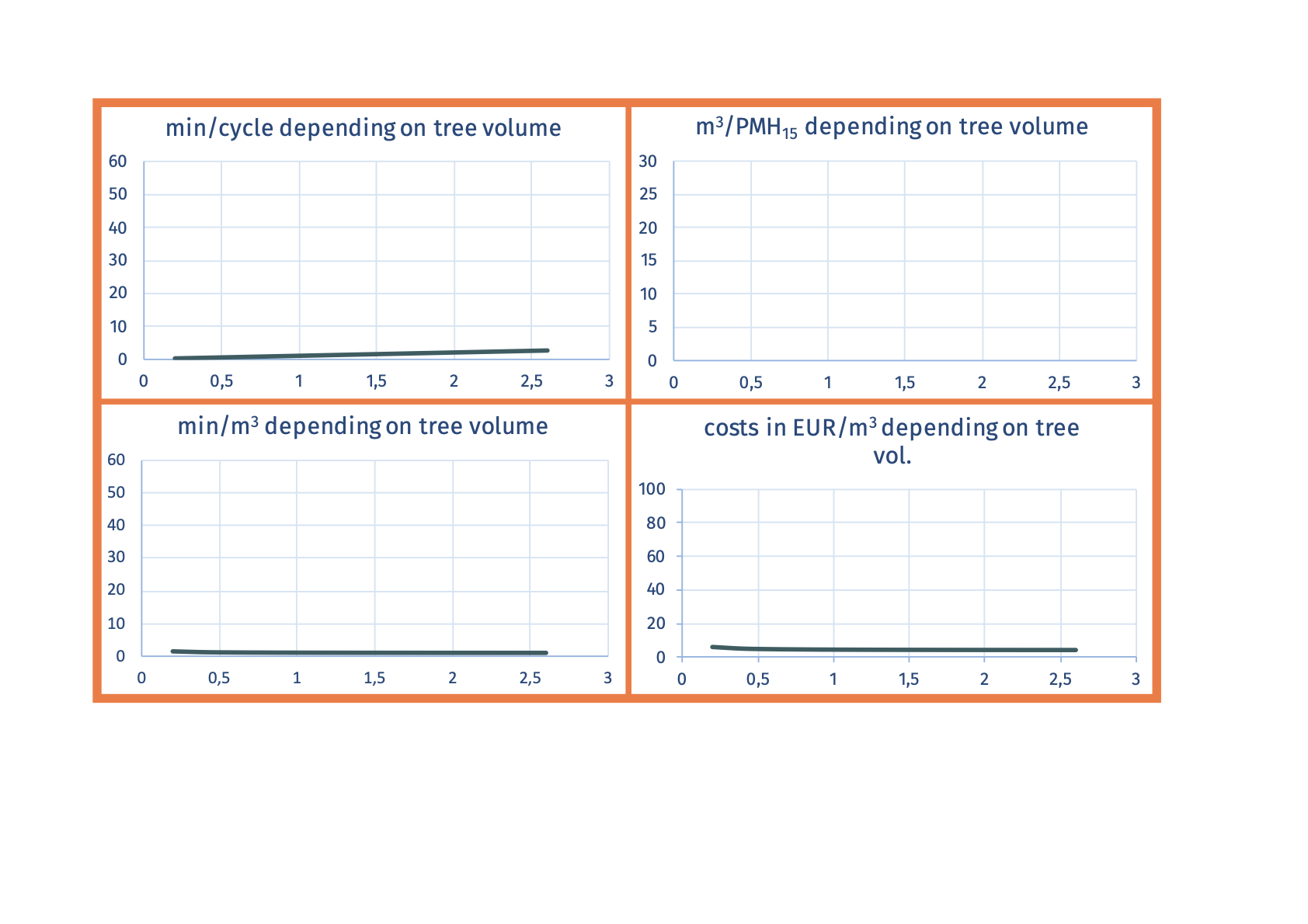 Ecogram
Social suitability:
| |
SP-x1-x2 manual delimbingLimbs are to be cut by axe or comparable knives: with one cut the branch should be separated - therefore more suitable for younger trees and conifer species 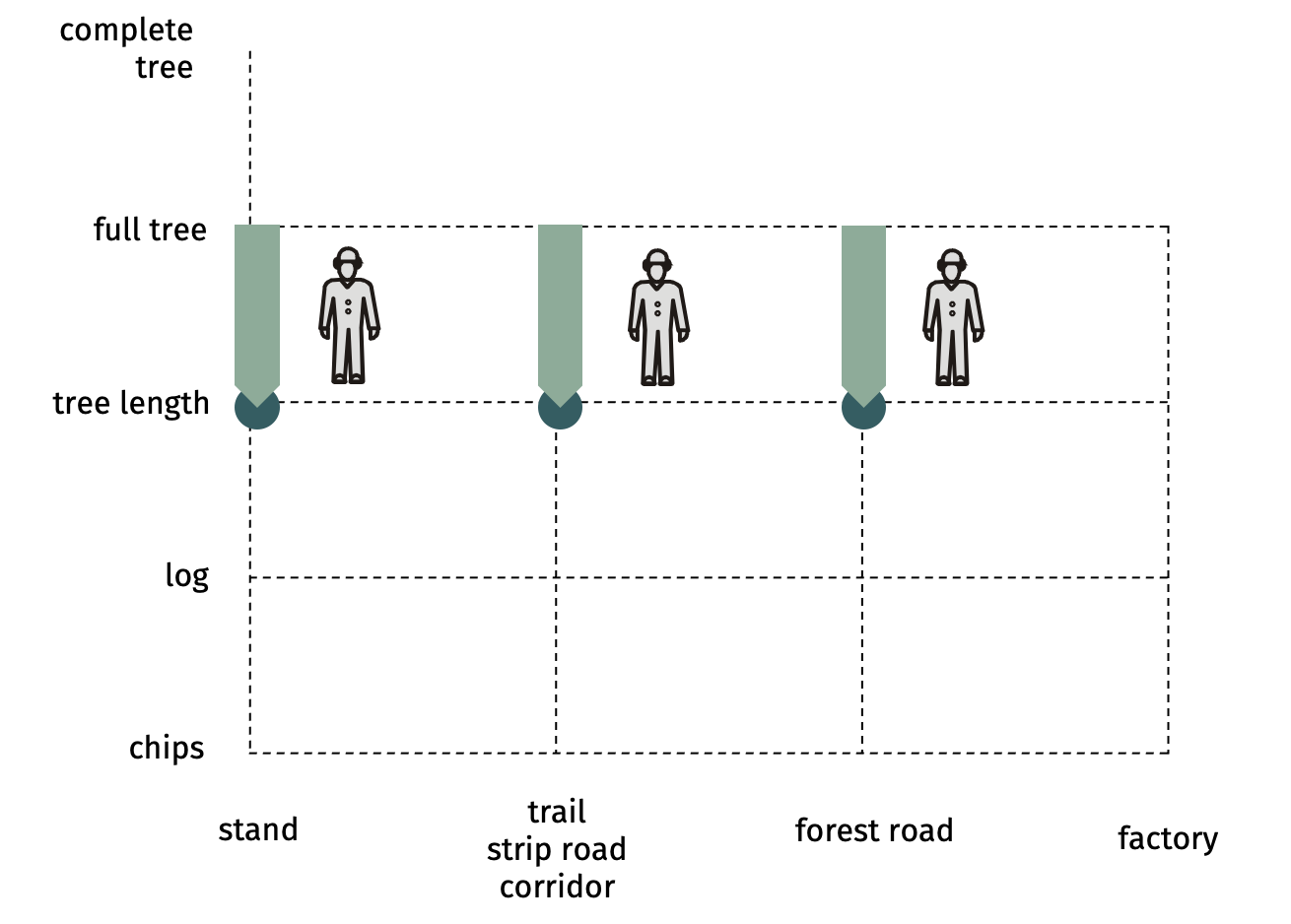 Advantages
Example:
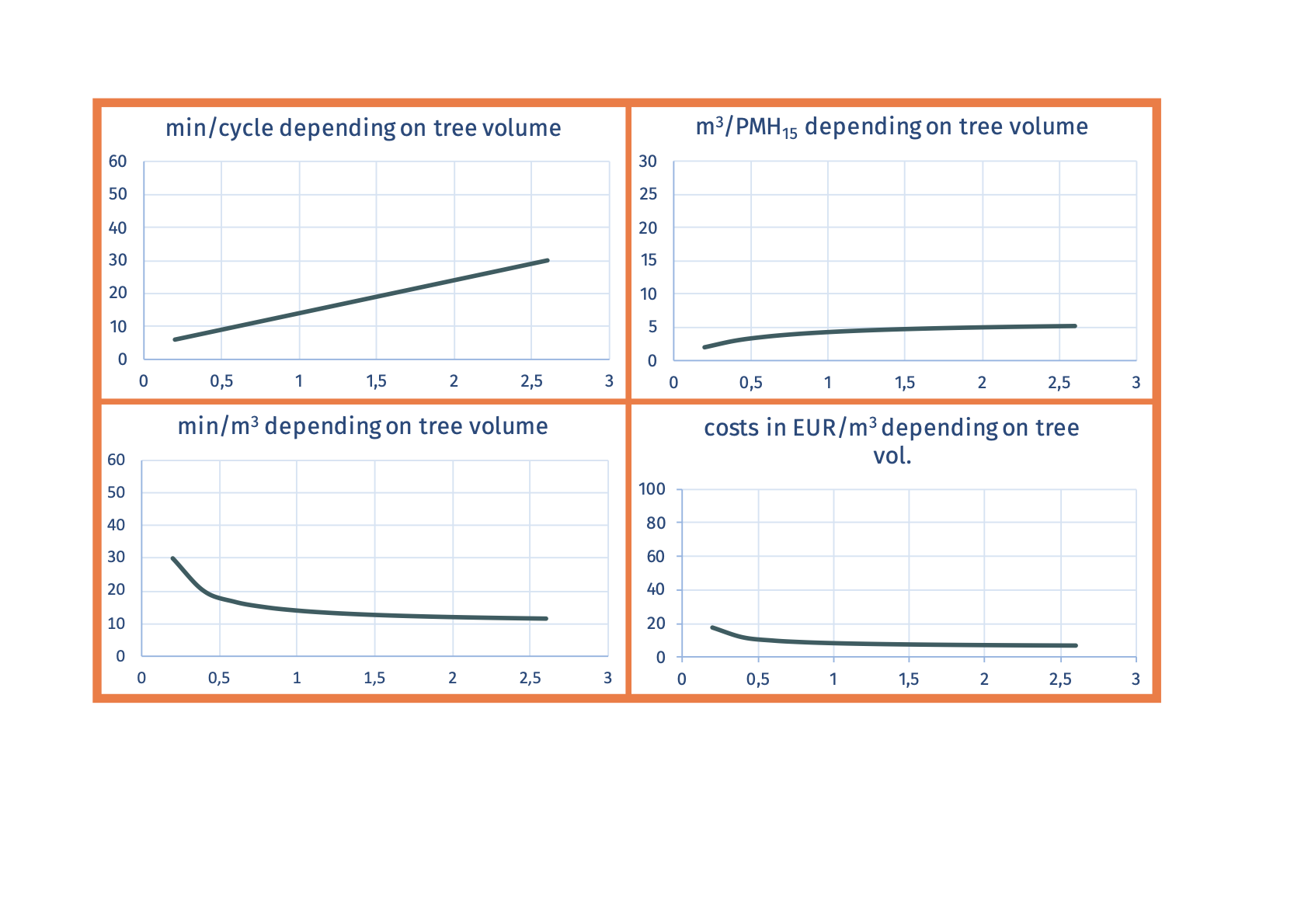
Social suitability
| |
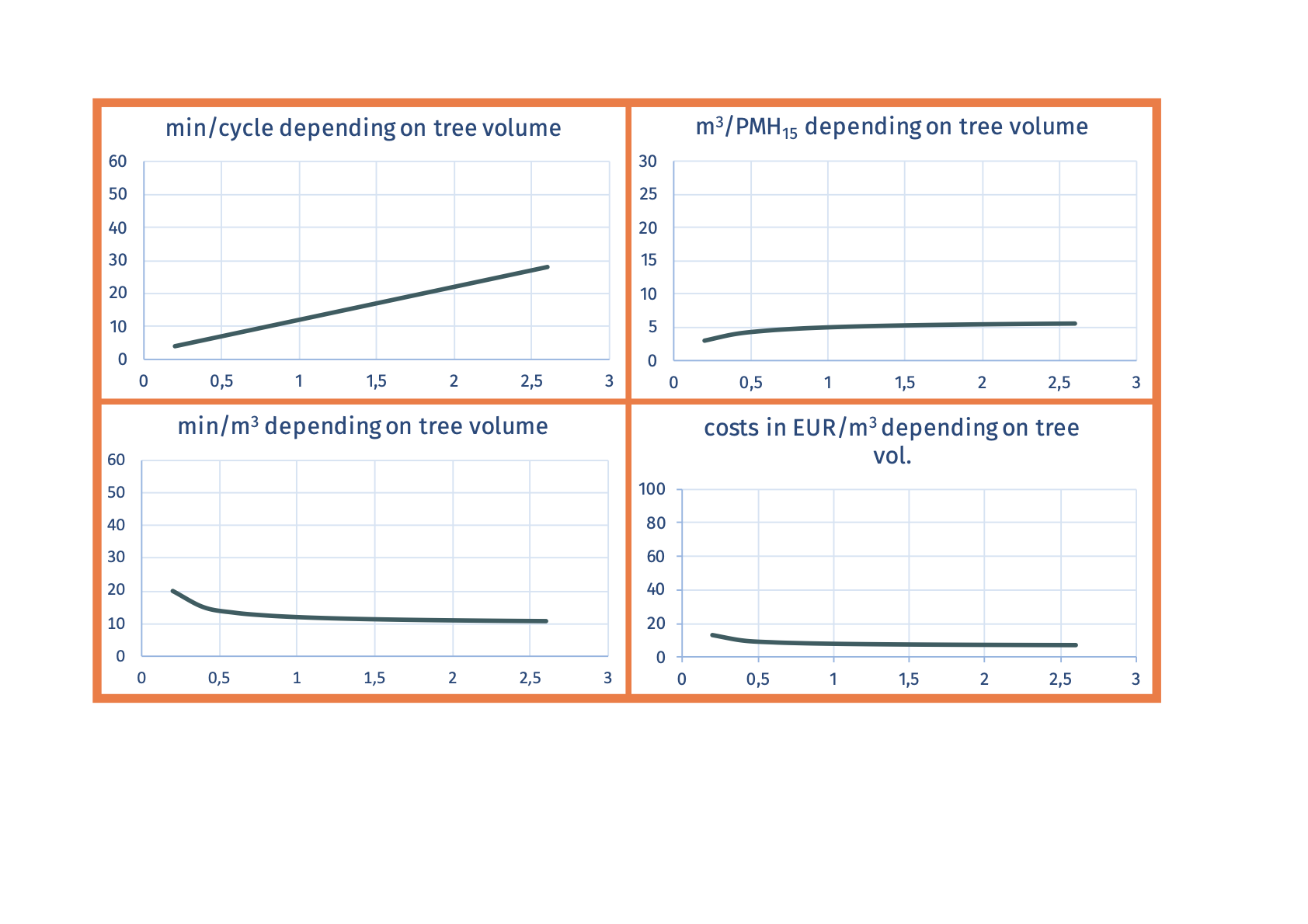
SP-x1-x2 motor-manual delimbingWhen the tree is felled (lays on ground) the limbs are cut from bottom to top. Three methods: 2 whorls at a time, whorl by whorl, and in the crown from top to the side. When finished turn the log and work the other side 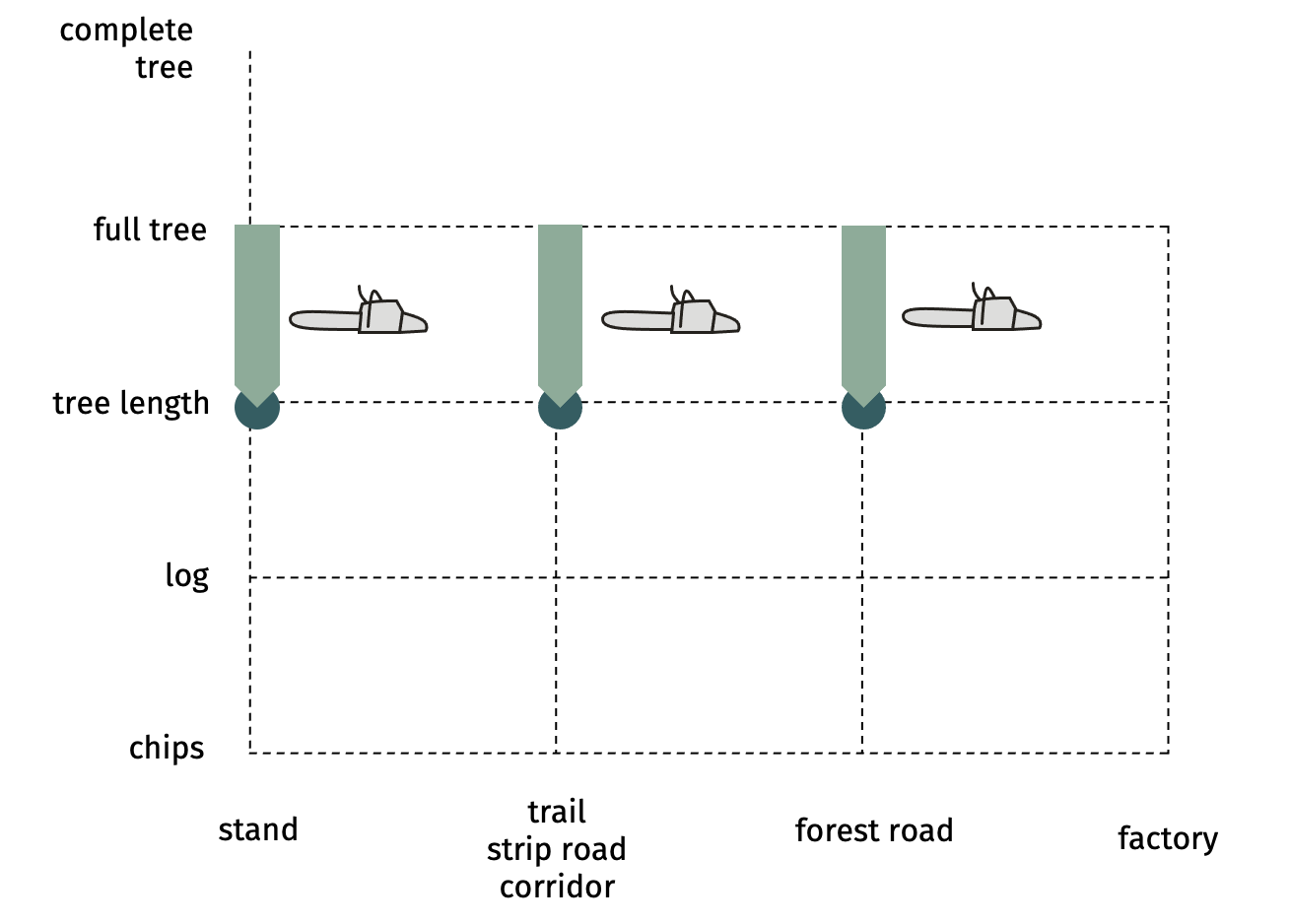 Advantages
Example:
 Ecogram
Social suitability
| |
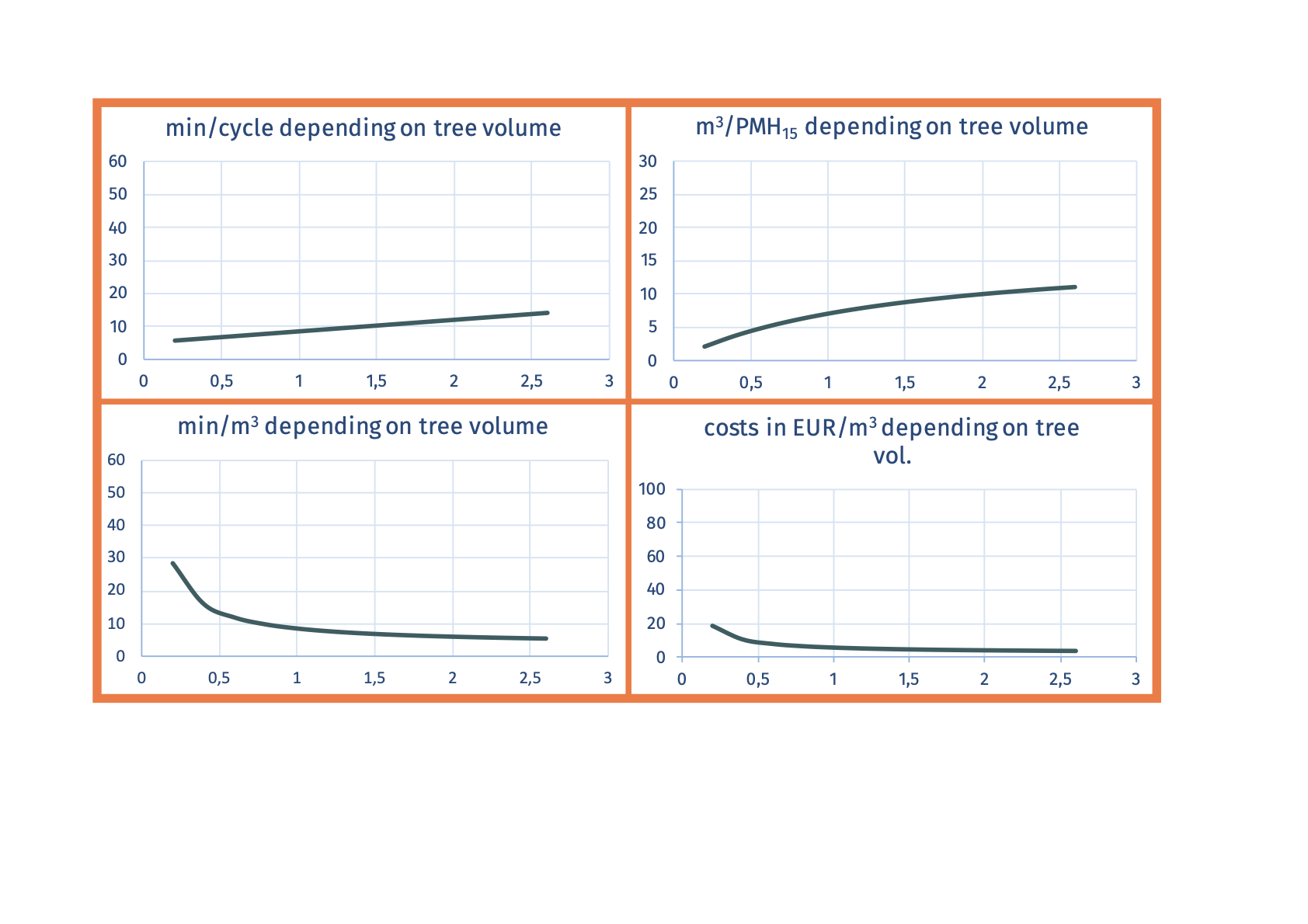
SP-x2-x3 motor-manual cross-cuttingAfter
measuring and decision where the optimal cuts have to be set, the trunk is cut into
2 or more pieces, (nearly) each of them marketable assortment. 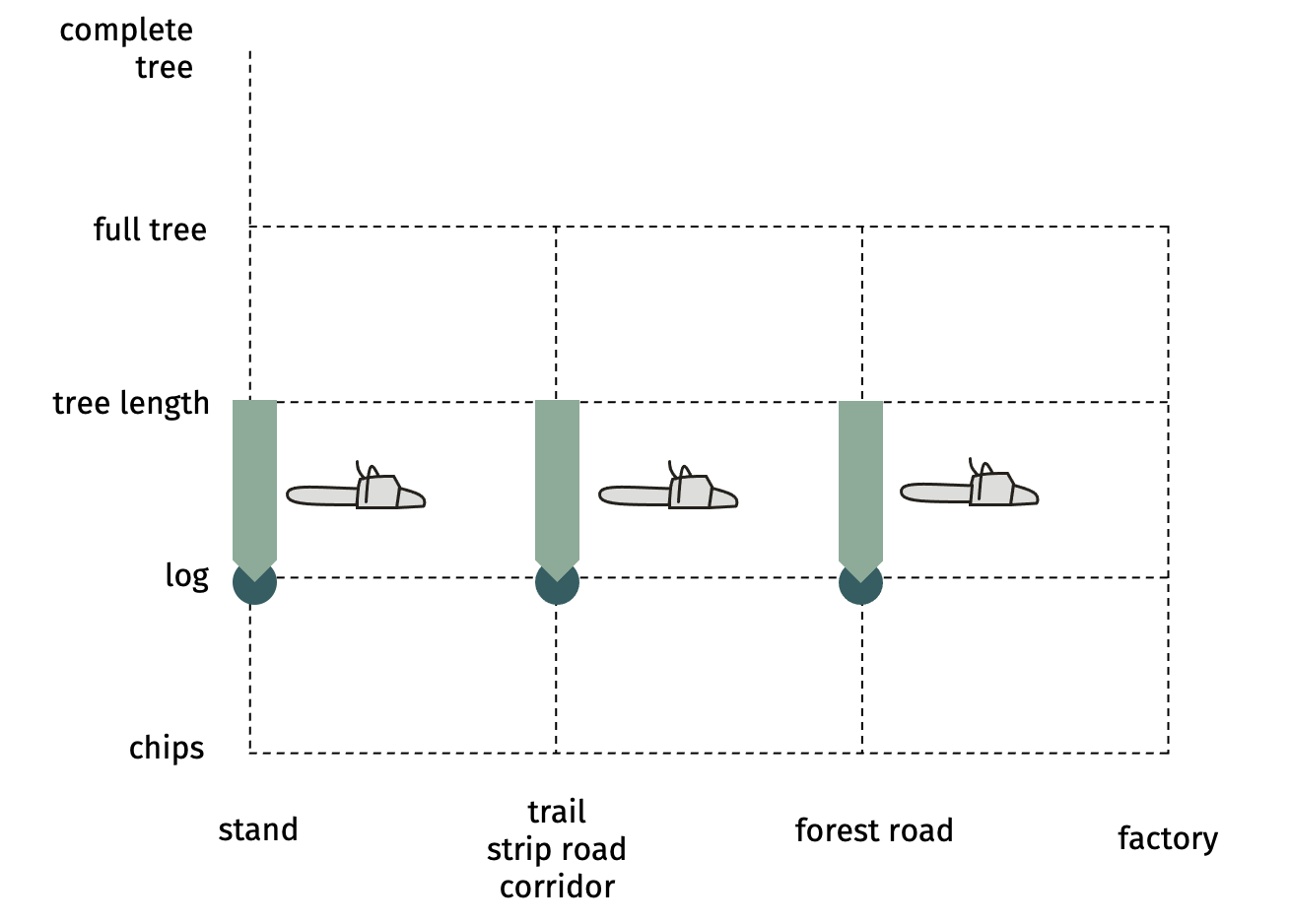 Advantages
Example:
Social suitability
| |